Repair of DNA Breaks by Break-Induced Replication
- PMID: 33792375
- PMCID: PMC9629446
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev-biochem-081420-095551
Repair of DNA Breaks by Break-Induced Replication
Abstract
Double-strand DNA breaks (DSBs) are the most lethal type of DNA damage, making DSB repair critical for cell survival. However, some DSB repair pathways are mutagenic and promote genome rearrangements, leading to genome destabilization. One such pathway is break-induced replication (BIR), which repairs primarily one-ended DSBs, similar to those formed by collapsed replication forks or telomere erosion. BIR is initiated by the invasion of a broken DNA end into a homologous template, synthesizes new DNA within the context of a migrating bubble, and is associated with conservative inheritance of new genetic material. This mode of synthesis is responsible for a high level of genetic instability associated with BIR. Eukaryotic BIR was initially investigated in yeast, but now it is also actively studied in mammalian systems. Additionally, a significant breakthrough has been made regarding the role of microhomology-mediated BIR in the formation of complex genomic rearrangements that underly various human pathologies.
Keywords: ALT; BIR; CRGs; DSBs; MMBIR; alternative lengthening of telomeres; break-induced replication; complex genome rearrangements; double-strand DNA breaks; microhomology-mediated break-induced replication.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest
Authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

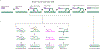

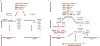
Similar articles
-
Break induced replication in eukaryotes: mechanisms, functions, and consequences.Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2017 Aug;52(4):395-413. doi: 10.1080/10409238.2017.1314444. Epub 2017 Apr 21. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28427283 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Break-Induced Replication: The Where, The Why, and The How.Trends Genet. 2018 Jul;34(7):518-531. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2018.04.002. Epub 2018 May 4. Trends Genet. 2018. PMID: 29735283 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Migrating bubble during break-induced replication drives conservative DNA synthesis.Nature. 2013 Oct 17;502(7471):389-92. doi: 10.1038/nature12584. Epub 2013 Sep 11. Nature. 2013. PMID: 24025772 Free PMC article.
-
Stressed? Break-induced replication comes to the rescue!DNA Repair (Amst). 2024 Oct;142:103759. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2024.103759. Epub 2024 Aug 30. DNA Repair (Amst). 2024. PMID: 39241677 Review.
-
Break-induced replication mechanisms in yeast and mammals.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2021 Dec;71:163-170. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2021.08.002. Epub 2021 Sep 1. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2021. PMID: 34481360 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Revisiting mutagenesis at non-B DNA motifs in the human genome.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2023 Apr;30(4):417-424. doi: 10.1038/s41594-023-00936-6. Epub 2023 Mar 13. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 36914796 Free PMC article.
-
RIOX1-demethylated cGAS regulates ionizing radiation-elicited DNA repair.Bone Res. 2022 Feb 24;10(1):19. doi: 10.1038/s41413-022-00194-0. Bone Res. 2022. PMID: 35210392 Free PMC article.
-
Rad53 regulates the lifetime of Rdh54 at homologous recombination intermediates.Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Nov 27;51(21):11688-11705. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad848. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023. PMID: 37850655 Free PMC article.
-
Telomere-related DNA damage response pathways in cancer therapy: prospective targets.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jun 7;15:1379166. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1379166. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38910895 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Homologous recombination deficiency (HRD) diagnostics: underlying mechanisms and new perspectives.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2024 Dec 26;44(1):19. doi: 10.1007/s10555-024-10238-y. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2024. PMID: 39724448 Review.
References
-
- Hoeijmakers JH. 2009. DNA damage, aging, and cancer. N Engl J Med 361: 1475–85 - PubMed
-
- Friedberg EC, Friedberg EC. 2006. DNA repair and mutagenesis. Washington, D.C.: ASM Press. xxix, 1118 p. pp.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

