Caloric and nutrient restriction to augment chemotherapy efficacy for acute lymphoblastic leukemia: the IDEAL trial
- PMID: 33792627
- PMCID: PMC8045487
- DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2020004018
Caloric and nutrient restriction to augment chemotherapy efficacy for acute lymphoblastic leukemia: the IDEAL trial
Abstract
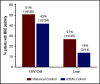
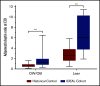
Being overweight or obese (OW/OB) during B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL) induction is associated with chemoresistance as quantified by minimal residual disease (MRD). We hypothesized that caloric and nutrient restriction from diet/exercise could lessen gains in fat mass (FM) and reduce postinduction MRD. The Improving Diet and Exercise in ALL (IDEAL) trial enrolled patients 10 to 21 years old, newly diagnosed with B-ALL (n = 40), in comparison with a recent historical control (n = 80). Designed to achieve caloric deficits ≥20% during induction, reduce fat intake/glycemic load, and increase activity, IDEAL's end points were FM gain (primary), MRD ≥0.01%, and adherence/feasibility. Integrated biology explored biomarkers of OW/OB physiology. IDEAL intervention did not significantly reduce median FM change from baseline overall (+5.1% [interquartile range [IQR], 15.8] vs +10.7% [IQR, 16.0]; P = .13), but stratified analysis showed benefit in those OW/OB (+1.5% [IQR, 6.6] vs +9.7% [IQR, 11.1]; P = .02). After accounting for prognostic factors, IDEAL intervention significantly reduced MRD risk (odds ratio, 0.30; 95% confidence interval, 0.09-0.92; P = .02). The trial exceeded its adherence (≥75% of overall diet) and feasibility (≥80% completed visits) thresholds. Integrated biology found the IDEAL intervention increased circulating adiponectin and reduced insulin resistance. The IDEAL intervention was feasible, decreased fat gain in those OW/OB, and reduced MRD. This is the first study in any hematologic malignancy to demonstrate potential benefit from caloric restriction via diet/exercise to augment chemotherapy efficacy and improve disease response. A prospective, randomized trial is warranted for validation. These trials were registered at www.clinicaltrials.gov as #NCT02708108 (IDEAL trial) and #NCT01317940 (historical control).
© 2021 by The American Society of Hematology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: E.O. served on an advisory board for Servier Pharmaceuticals outside of the scope of this work. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Larsson SC, Wolk A. Overweight and obesity and incidence of leukemia: a meta-analysis of cohort studies. Int J Cancer. 2008;122(6):1418-1421. - PubMed
-
- Calle EE, Rodriguez C, Walker-Thurmond K, Thun MJ. Overweight, obesity, and mortality from cancer in a prospectively studied cohort of U.S. adults. N Engl J Med. 2003;348(17):1625-1638. - PubMed
-
- Butturini AM, Dorey FJ, Lange BJ, et al. . Obesity and outcome in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25(15):2063-2069. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

