The genus Anaplasma: drawing back the curtain on tick-pathogen interactions
- PMID: 33792663
- PMCID: PMC8062235
- DOI: 10.1093/femspd/ftab022
The genus Anaplasma: drawing back the curtain on tick-pathogen interactions
Abstract
Tick-borne illnesses pose a serious concern to human and veterinary health and their prevalence is on the rise. The interactions between ticks and the pathogens they carry are largely undefined. However, the genus Anaplasma, a group of tick-borne bacteria, has been instrumental in uncovering novel paradigms in tick biology. The emergence of sophisticated technologies and the convergence of entomology with microbiology, immunology, metabolism and systems biology has brought tick-Anaplasma interactions to the forefront of vector biology with broader implications for the infectious disease community. Here, we discuss the use of Anaplasma as an instrument for the elucidation of novel principles in arthropod-microbe interactions. We offer an outlook of the primary areas of study, outstanding questions and future research directions.
Keywords: Anaplasma; arthropod vectors; ehrlichia; orientia; rickettsia; tick-borne diseases.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of FEMS.
Figures

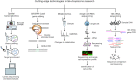
References
-
- Ahantarig A, Trinachartvanit W, Baimai Vet al. . Hard ticks and their bacterial endosymbionts (or would be pathogens). Folia Microbiol (Praha). 2013;58:419–28. - PubMed
-
- Atif FA. Anaplasma marginale and Anaplasma phagocytophilum: rickettsiales pathogens of veterinary and public health significance. Parasitol Res. 2015;114:3941–57. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

