Examining therapeutic equivalence between branded and generic warfarin in Brazil: The WARFA crossover randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 33793580
- PMCID: PMC8016229
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0248567
Examining therapeutic equivalence between branded and generic warfarin in Brazil: The WARFA crossover randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Objectives: To determine whether the generic and branded warfarins used as anticoagulants in Brazil are therapeutic equivalents based on their international normalized ratio (INR) results.
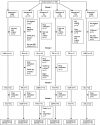
Methods: This crossover randomized controlled trial had four periods. We used the branded Marevan and two generic versions of warfarin sodium tablets, manufactured by União Química and Teuto laboratories, all purchased from retail drugstores. Eligible participants were outpatients from an anticoagulation clinic at a university hospital in São Paulo, Brazil. They had atrial fibrillation or flutter and had been using warfarin for at least 2 months with an INR therapeutic range of 2.0-3.0. Randomization was by numbered, opaque, sealed envelopes. Healthcare personnel and outcome assessors were blinded to treatments, but patients were not. The primary outcome was the variability in the INR (ΔINR) and secondary outcomes included mean INR. We accepted formulations as equivalent if the 95% confidence interval (CI) of the comparison of ΔINR between branded and generic formulations was within the limit of ±0.49.
Results: One hundred patients were recruited and randomized to six sequences of treatment (four sequences with n = 17 and two sequences with n = 16). União Química generic warfarin had equivalent variability in the INR to Marevan (ΔINR +0.09 [95% CI -0.29 to +0.46], n = 84). Comparison between Teuto generic warfarin and Marevan was inconclusive (ΔINR +0.29 [95% CI -0.09 to +0.68], n = 84).
Conclusions: Marevan and União Química warfarin had equivalent therapeutic effectiveness and both could be confidently used for anticoagulation. The comparison between Marevan and TW was inconclusive and does not warrant a statement of equivalence. Our methods are especially important for comparing generic and branded drugs that raise concerns and may be subject of future investigations by regulatory agents.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT02017197.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Henderson JD, Esham RH. Generic substitution: issues for problematic drugs. South Med J. 2001;94(1):16–21. - PubMed
-
- Namazi MH, Yousefi ZK, Shirazi MG, Shaykholeslami M, Vakili H, Moatamedi MR, et al. Comparison of the clinical efficacy of three brands of warfarin. Indian J Pharmacol. 2004;36(6):360–2.
-
- Neutel JM, Smith DH. A randomized crossover study to compare the efficacy and tolerability of Barr warfarin sodium to the currently available Coumadin. Cardiovasc Rev Rep. 1998;19(2):49–59.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

