Effect of prolactin on normal and keratoconus human corneal stromal fibroblasts in vitro
- PMID: 33793669
- PMCID: PMC8016287
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0249344
Effect of prolactin on normal and keratoconus human corneal stromal fibroblasts in vitro
Abstract
Purpose: To examine the effect of prolactin (PRL) on human corneal stromal fibroblasts (CSFs), derived from healthy individuals and from keratoconus (KC) patients, in vitro, specifically assessing physiological and elevated PRL concentrations as apparent during pregnancy.
Methods: Eye bank corneas of 3 female and 3 male healthy individuals as well as the corneal buttons of 3 female and 3 male KC patients were utilized for this study. The endothelium of the cornea was removed with sterile surgical scalpels, the probes were washed repeatedly with Dulbecco's PBS and corneoscleral rims were trimmed off. Subsequently the corneal stroma was digested with collagenase type I and the harvested CSFs were cultured. We then examined (1) cell proliferation, (2) cell viability and (3) cytokine release of CSFs upon exposure to prolactin in vitro.
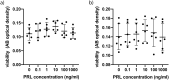
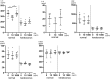
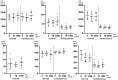
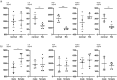
Results: With respect to viability and proliferation our experiments did not show significant differences between CSFs exposed to different PRL concentrations. Our data show a significantly lower IL-8 concentration in normal CSFs exposed to 10ng/ml PRL compared to 0ng/ml and 1000ng/ml at 5 hours post exposition. Moreover, we can report significantly lower secretion of IL-8, IL-6, HGF, VEGF and FGFb in KC CSFs compared to normal CSFs, independent of PRL exposure, as determined by cytokine ELISA.
Conclusion: Our data in part points towards corneal cytokine secretion as a possible link between altered stromal PRL concentrations and KC progression. However, in our small dataset a significant influence of PRL concentration on cytokine secretion can only be described for IL-8 in normal CSFs. Further our results contribute to existing reports on the importance of cytokines in KC development, with an emphasis on significantly lower cytokine secretion in KC CSFs compared to normal controls.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

