Shouting out loud: signaling modules in the regulation of stomatal development
- PMID: 33793896
- PMCID: PMC8133662
- DOI: 10.1093/plphys/kiaa061
Shouting out loud: signaling modules in the regulation of stomatal development
Abstract
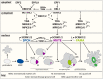
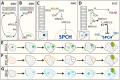
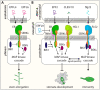
Stomata are small pores on the surface of land plants that facilitate gas exchange for photosynthesis while minimizing water loss. The function of stomata is pivotal for plant growth and survival. Intensive research on the model plant Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana) has discovered key peptide signaling pathways, transcription factors, and polarity components that together drive proper stomatal development and patterning. In this review, we focus on recent findings that have revealed co-option of peptide-receptor kinase signaling modules-utilized for diverse developmental processes and immune response. We further discuss an emerging connection between extrinsic signaling and intrinsic polarity modules. These findings have further enlightened our understanding of this fascinating developmental process.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of American Society of Plant Biologists.
Figures

References
-
- Aan den Toorn M, Albrecht C, de Vries S (2015) On the origin of SERKs: bioinformatics analysis of the somatic embryogenesis receptor kinases. Mol Plant 8:762–782 - PubMed
-
- Abrash EB, Bergmann DC (2010) Regional specification of stomatal production by the putative ligand CHALLAH. Development 137:447–455 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

