[The development of consonant perception in pediatric cochlear implants of 1-3 years old]
- PMID: 33794634
- PMCID: PMC10128445
- DOI: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2021.04.013
[The development of consonant perception in pediatric cochlear implants of 1-3 years old]
Abstract
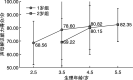
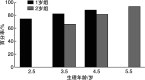
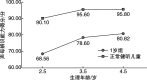
Objective:To explore the development of consonant perception in early implanted pediatric with prelingual bilateral profound sensorineural hearing loss at 1 to 3 years of age. Methods:A retrospective study was conducted to prospectively analyze the pediatric with hearing impaired who had cochlear implantation. According to the age of implantation, all participants were divided into two groups as 1 year old group(1-<2) and 2 years old group(2-<3). It was compared the consonant perception of Mandarin early speech perception test scores at 1, 2, 3 years after implantation as well as the trends in consonant perception between 1 year old group and normal hearing pediatrics of the same age. Results:①The scores improved notably in two groups with the increase of physiological age(P=0.038, P=0.012); ②The consonant perception of 1 year old group was significantly better than that of 2 years old group(P<0.05), however, there are great difference between 1 year old group and normal hearing pediatrics of the same age. Conclusion:With the increase of physiological age, the consonant perception will be improved correspondingly within 3 years of pediatric cochlear implants under the age of 3 however there are differences with normal hearing pediatrics of the same age; the earlier the age of implant, the better the consonant perception is.
目的:初步探讨植入年龄为1~3岁行单侧人工耳蜗植入术(CI)的语前双耳极重度感音神经性听力损失儿童术后3年内声母辨识能力的发育规律。 方法:采用回顾性研究的方法,分析完成CI开机的听力损失儿童声母辨识能力的相关情况。根据植入年龄分为1岁组(1~<2岁)和2岁组(2~<3岁)。采用普通话早期言语感知测试,在开机后1、2、3年时测试CI儿童声母辨识能力,并将1岁组与同龄健听儿童的声母辨识能力的发展趋势进行对比。 结果:①两组CI儿童的声母辨识能力均随着生理年龄的增长而显著提高(P=0.038,P=0.012);②1岁组的声母辨识能力明显高于2岁组(P<0.05),但与同龄健听儿童相比还存在很大的差异。 结论:术后3年内,植入年龄小于3岁的儿童随着CI佩戴时间的增加其声母辨识能力均有相应提高,但与同龄健听儿童相比还存在着一定的差异;植入年龄越小,声母辨识能力越好。.
Keywords: child; cochlear implantation; consonant perception; prelingual deafness.
Copyright© by the Editorial Department of Journal of Clinical Otorhinolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors of this article and the planning committee members and staff have no relevant financial relationships with commercial interests to disclose.
Figures
References
-
-
黄伯荣, 廖序东. 语音概说[M]//黄伯荣, 廖序东. 现代汉语增订版. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2017: 23-28.
-
-
-
韩德民, 许时昂. 小儿听力言语语言康复及聋儿教育[M]//韩德民, 许时昂. 听力学基础与临床. 北京: 科学技术文献出版社, 2004: 472-477.
-
-
- 刘 洁芬, 吴 立平, 宋 晓华, et al. 聋童语音的声学参数分析. 中国特殊教育. 1999;(2):16–19.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical