Feedback activation of NF-KB signaling leads to adaptive resistance to EZH2 inhibitors in prostate cancer cells
- PMID: 33794893
- PMCID: PMC8017762
- DOI: 10.1186/s12935-021-01897-w
Feedback activation of NF-KB signaling leads to adaptive resistance to EZH2 inhibitors in prostate cancer cells
Abstract
Background: Prostate cancer (PCa) is the most common malignant tumor in developed countries, which has seriously threatened men's lifestyle and quality of life. The up-regulation of EZH2 is associated with advanced PCa and poor prognosis, making it a promising therapeutic target. However, the EZH2 inhibitors-based treatment is basically ineffective against PCa, which limits its clinical application.
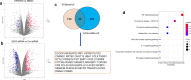
Methods: Microarray data (GSE107779) from LNCaP cells treated with either siRNA against EZH2 or a EZH2 inhibitor EPZ6438 was analyzed by Limma R package. Western blot, real-time PCR and luciferase reporter assays were used to determine the EZH2-SOX9-TNFRSF11A axis and the activity of NF-κB signaling in PCa cells. CCK-8 assay was used to determine the viability of PCa cells following various treatments.
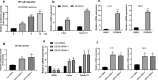
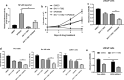
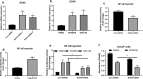
Results: Genetic ablation or pharmacological inhibition of EZH2 leads to feedback activation of NF-κB signaling in PCa cells. EZH2-dependent SOX9 expression regulates the activation of NF-κB signaling. TNFRSF11A, also known as receptor activator of NF-κB (RANK), is a downstream target of SOX9 in PCa cells. SOX9 recognizes two putative SOX9 response elements in the promoter region of TNFRSF11A gene to drive TNFRSF11A expression and downstream NF-κB signaling activation. Suppression of the NF-κB signaling by either TNFRSF11A silencing or BAY11-7082 treatment rendered PCa cells to EZH2 inhibitors.
Conclusion: Collectively, our finding reveals a EZH2-SOX9-TNFRSF11A axis in the regulation of activity of NF-κB signaling in PCa cells and suggests that a combination of EZH2 inhibitors and BAY11-7082 would be an effective approach for the treatment of PCa patients in the future.
Keywords: EZH2; NF-κB; Prostate cancer (PCa); SOX9; TNFRSF11A (RANK).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Involvement of aberrantly activated HOTAIR/EZH2/miR-193a feedback loop in progression of prostate cancer.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2017 Nov 15;36(1):159. doi: 10.1186/s13046-017-0629-7. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 29141691 Free PMC article.
-
Nemo-like kinase as a negative regulator of nuclear receptor Nurr1 gene transcription in prostate cancer.BMC Cancer. 2016 Mar 31;16:257. doi: 10.1186/s12885-016-2291-4. BMC Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27036119 Free PMC article.
-
Ectopic fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 promotes inflammation by promoting nuclear factor-κB signaling in prostate cancer cells.J Biol Chem. 2018 Sep 21;293(38):14839-14849. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.002907. Epub 2018 Aug 9. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 30093411 Free PMC article.
-
Recent insights into NF-κB signalling pathways and the link between inflammation and prostate cancer.BJU Int. 2014 Aug;114(2):168-76. doi: 10.1111/bju.12488. Epub 2014 Feb 20. BJU Int. 2014. PMID: 24215139 Review.
-
Interplay Between SOX9, Wnt/β-Catenin and Androgen Receptor Signaling in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Apr 26;20(9):2066. doi: 10.3390/ijms20092066. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31027362 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
EZH2 loss during metabolic stress drives restoration of MHC class I machinery in melanoma.iScience. 2025 May 26;28(6):112750. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2025.112750. eCollection 2025 Jun 20. iScience. 2025. PMID: 40546964 Free PMC article.
-
The Pivotal Immunomodulatory and Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Histone-Lysine N-Methyltransferase in the Glioma Microenvironment: Its Biomarker and Therapy Potentials.Anal Cell Pathol (Amst). 2021 Oct 27;2021:4907167. doi: 10.1155/2021/4907167. eCollection 2021. Anal Cell Pathol (Amst). 2021. PMID: 34745848 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Early host immune responses in a human organoid-derived gallbladder monolayer to Salmonella Typhi strains from patients with acute and chronic infections: a comparative analysis.Front Immunol. 2024 Mar 12;15:1334762. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1334762. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38533492 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic Inflammation Pathway NF-κB Cooperates with Epigenetic Reprogramming to Drive the Malignant Progression of Glioblastoma.Int J Biol Sci. 2022 Sep 21;18(15):5770-5786. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.73749. eCollection 2022. Int J Biol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36263173 Free PMC article.
-
Simultaneous administration of EZH2 and BET inhibitors inhibits proliferation and clonogenic ability of metastatic prostate cancer cells.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2023 Dec;38(1):2163242. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2022.2163242. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 36629431 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

