Pathophysiology of SARS-CoV-2: the Mount Sinai COVID-19 autopsy experience
- PMID: 33795830
- PMCID: PMC8015313
- DOI: 10.1038/s41379-021-00793-y
Pathophysiology of SARS-CoV-2: the Mount Sinai COVID-19 autopsy experience
Abstract
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and its associated clinical syndrome COVID-19 are causing overwhelming morbidity and mortality around the globe and disproportionately affected New York City between March and May 2020. Here, we report on the first 100 COVID-19-positive autopsies performed at the Mount Sinai Hospital in New York City. Autopsies revealed large pulmonary emboli in six cases. Diffuse alveolar damage was present in over 90% of cases. We also report microthrombi in multiple organ systems including the brain, as well as hemophagocytosis. We additionally provide electron microscopic evidence of the presence of the virus in our samples. Laboratory results of our COVID-19 cohort disclose elevated inflammatory markers, abnormal coagulation values, and elevated cytokines IL-6, IL-8, and TNFα. Our autopsy series of COVID-19-positive patients reveals that this disease, often conceptualized as a primarily respiratory viral illness, has widespread effects in the body including hypercoagulability, a hyperinflammatory state, and endothelial dysfunction. Targeting of these multisystemic pathways could lead to new treatment avenues as well as combination therapies against SARS-CoV-2 infection.
© 2021. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to United States & Canadian Academy of Pathology.
Figures
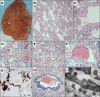
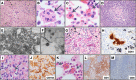

References
-
- COVID-19 Dashboard by the Center for Systems Science and Engineering (CSSE) at Johns Hopkins University, [Internet]. [Accessed 21 Jan 2021]. Available from https://coronavirus.jhu.edu.
-
- Carsana L, Sonzogni A, Nasr A, Rossi RS, Pellegrinelli A, Zerbi P, et al. Pulmonary post-mortem findings in a series of COVID-19 cases from northern Italy: a two-centre descriptive study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2020;20:1135–1140. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30434-5. PMCID 7279758, PubMed PMID: 32526193. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fox SE, Akmatbekov A, Harbert JL, Li G, Quincy Brown J, Vander Heide RS. Pulmonary and cardiac pathology in African American patients with COVID-19: an autopsy series from New Orleans. Lancet Respir Med. 2020;8:681–686. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30243-5. PMCID 7255143, PubMed PMID: 32473124. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

