Interstitial lung abnormality (ILA) and nonspecific interstitial pneumonia (NSIP)
- PMID: 33796637
- PMCID: PMC7995484
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejro.2021.100336
Interstitial lung abnormality (ILA) and nonspecific interstitial pneumonia (NSIP)
Abstract
This review article aims to address mysteries existing between Interstitial Lung Abnormality (ILA) and Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia (NSIP). The concept and definition of ILA are based upon CT scans from multiple large-scale cohort studies, whereas the concept and definition of NSIP originally derived from pathology with evolution to multi-disciplinary diagnosis. NSIP is the diagnosis as Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD) with clinical significance, whereas only a part of subjects with ILA have clinically significant ILD. Eventually, both ILA and NSIP must be understood in the context of chronic fibrosing ILD and progressive ILD, which remains to be further investigated.
Keywords: AIP, acute interstitial pneumonia; ATS/ERS, American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society; BIP, bronchiolitis obliterans with interstitial pneumonia; BOOP, bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia; CT; CTD, connective tissue disease; Connective tissue disease (CTD); DIP, desquamative interstitial pneumonia; GGO, ground-glass opacities; GIP, giant cell interstitial pneumonia; HRCT; HRCT, high-resolution CT; IIP, idiopathic interstitial pneumonia; ILA, interstitial lung abnormality; ILD, interstitial lung disease; Interstitial lung abnormality (ILA); Interstitial lung disease (ILD); LIP, lymphoid interstitial pneumonia; NSIP, nonspecific interstitial pneumonia; Nonspecific interstitial pneumonia (NSIP); Pulmonary fibrosis; RB-ILD, respiratory bronchiolitis-associated interstitial lung disease; UIP, usual interstitial pneumonia; fNSIP, fibrosing nonspecific interstitial pneumonia.
© 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Hatabu reports grants from Canon Medical Systems Inc, grants from Konica Minolta Inc, personal fees from Mitsubishi Chemical Co, personal fees from Canon Medical Systems Inc, outside the submitted work. Other authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
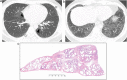
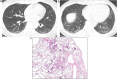
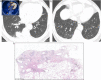
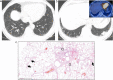
References
-
- Hatabu H., Hunninghake G.M., Richeldi L., Brown K.K., Wells A.U., Remy-Jardin M., Verschakelen J., Nicholson A.G., Beasley M.B., Christiani D.C., San José Estépar R., Seo J.B., Johkoh T., Sverzellati N., Ryerson C.J., Graham Barr R., Goo J.M., Austin J.H.M., Powell C.A., Lee K.S., Inoue Y., Lynch D.A. Interstitial lung abnormalities detected incidentally on CT: a position paper from the Fleischner Society. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020;8:726–737. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30168-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- American Thoracic Society, European Respiratory Society American thoracic Society/European respiratory society international multidisciplinary consensus classification of the idiopathic interstitial pneumonias. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002;165:277–304. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.165.2.ats01. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hino T., Lee K.S., Han J., Hata A., Ishigami K., Hatabu H. Spectrum of pulmonary fibrosis from interstitial lung abnormality to usual interstitial pneumonia: importance of identification and quantification of traction bronchiectasis in patient management. Korean J. Radiol. 2020;21 (online ahead of print) - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

