FOXO regulates the expression of antimicrobial peptides and promotes phagocytosis of hemocytes in shrimp antibacterial immunity
- PMID: 33798239
- PMCID: PMC8046353
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1009479
FOXO regulates the expression of antimicrobial peptides and promotes phagocytosis of hemocytes in shrimp antibacterial immunity
Erratum in
-
Correction: FOXO regulates the expres sion of antimicrobial peptides and promotes phagocytosis of hemocytes in shrimp antibacterial immunity.PLoS Pathog. 2025 Dec 16;21(12):e1013778. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1013778. eCollection 2025 Dec. PLoS Pathog. 2025. PMID: 41401130 Free PMC article.
Abstract
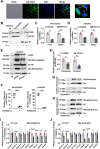
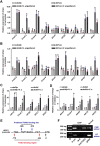
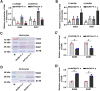
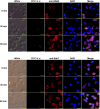
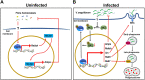
Invertebrates rely on innate immunity, including humoral and cellular immunity, to resist pathogenic infection. Previous studies showed that forkhead box transcription factor O (FOXO) participates in mucosal immune responses of mammals and the gut humoral immune regulation of invertebrates. However, whether FOXO is involved in systemic and cellular immunity regulation in invertebrates remains unknown. In the present study, we identified a FOXO from shrimp (Marsupenaeus japonicus) and found that it was expressed at relatively basal levels in normal shrimp, but was upregulated significantly in shrimp challenged by Vibrio anguillarum. FOXO played a critical role in maintaining hemolymph and intestinal microbiota homeostasis by promoting the expression of Relish, the transcription factor of the immune deficiency (IMD) pathway for expression of antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) in shrimp. We also found that pathogen infection activated FOXO and induced its nuclear translocation by reducing serine/threonine kinase AKT activity. In the nucleus, activated FOXO directly regulated the expression of its target Amp and Relish genes against bacterial infection. Furthermore, FOXO was identified as being involved in cellular immunity by promoting the phagocytosis of hemocytes through upregulating the expression of the phagocytotic receptor scavenger receptor C (Src), and two small GTPases, Rab5 and Rab7, which are related to phagosome trafficking to the lysosome in the cytoplasm. Taken together, our results indicated that FOXO exerts its effects on homeostasis of hemolymph and the enteric microbiota by activating the IMD pathway in normal shrimp, and directly or indirectly promoting AMP expression and enhancing phagocytosis of hemocytes against pathogens in bacteria-infected shrimp. This study revealed the different functions of FOXO in the mucosal (local) and systemic antibacterial immunity of invertebrates.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures





References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

