Expression of CD40L on CD4+T cells distinguishes active versus inactive HIV-associated Kaposi's Sarcoma
- PMID: 33799006
- PMCID: PMC8127409
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ctarc.2021.100361
Expression of CD40L on CD4+T cells distinguishes active versus inactive HIV-associated Kaposi's Sarcoma
Abstract
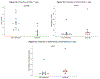
Kaposi's sarcoma (KS) is a malignancy of vascular origin. It is caused by the Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpes virus (KSHV). Immune dysregulation is a key feature in the development and progression of KS. The main aim of this study was to determine and compare circulating CD4+ and CD8+T cell subsets including their expression of CD40 ligand (CD40L) and programmed cell death protein 1 (PD1), natural killer (NK) cells, and NK T cells between individuals with active HIV-associated KS versus those in remission. We found that the proportion of CD4+T cells was significantly higher in individuals in remission compared to those with active KS (26.3% vs 13.9%; p = 0.01). We also observed that the proportion of CD4+T cells and central memory CD4+T cells expressing CD40L was significantly higher in individuals with active KS versus those in remission, (10.6% vs 5.4%; p = 0.03) and (14.8% vs 5.9%; p = 0.01) respectively. There was no significant difference in proportion of CD4+ and CD8+ naïve, central memory, effector memory, and terminal effector cells between the two groups. In addition, there was no difference in expression of PD1 on the T cell subsets between the two groups. Furthermore, the proportion of NK cells and NK T cells were not differential between individuals with active disease versus those in remission. CD40L expression is higher in individuals with active HIV-associated KS compared to those in remission. The proportion of CD4+T cells is higher in individuals in remission compared to those with active HIV-associated KS.
Keywords: CD40L; HIV; Kaposi's sarcoma; Natural killer cells; PD1; T cell subsets.
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Innis-Whitehouse W, Wang X, Restrepo N, Salas C, Moreno K, Restrepo A, et al. Kaposi sarcoma incidence in females is nearly four-fold higher in the Lower Rio Grande Valley compared to the Texas average. Cancer Treat Res Commun. 2018;16:45–52. - PubMed
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68(6):394–424. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

