Proteomics Profiling of Neuron-Derived Small Extracellular Vesicles from Human Plasma: Enabling Single-Subject Analysis
- PMID: 33799461
- PMCID: PMC7999506
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22062951
Proteomics Profiling of Neuron-Derived Small Extracellular Vesicles from Human Plasma: Enabling Single-Subject Analysis
Abstract
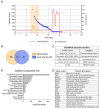
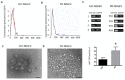
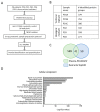
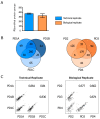
Small extracellular vesicles have been intensively studied as a source of biomarkers in neurodegenerative disorders. The possibility to isolate neuron-derived small extracellular vesicles (NDsEV) from blood represents a potential window into brain pathological processes. To date, the absence of sensitive NDsEV isolation and full proteome characterization methods has meant their protein content has been underexplored, particularly for individual patients. Here, we report a rapid method based on an immunoplate covalently coated with mouse monoclonal anti-L1CAM antibody for the isolation and the proteome characterization of plasma-NDsEV from individual Parkinson's disease (PD) patients. We isolated round-shaped vesicles with morphological characteristics consistent with exosomes. On average, 349 ± 38 protein groups were identified by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) analysis, 20 of which are annotated in the Human Protein Atlas as being highly expressed in the brain, and 213 were shared with a reference NDsEV dataset obtained from cultured human neurons. Moreover, this approach enabled the identification of 23 proteins belonging to the Parkinson disease KEGG pathway, as well as proteins previously reported as PD circulating biomarkers.
Keywords: L1CAM; NES cells; Parkinson’s disease; central nervous system; exosomes; miR-155; neuron-derived vesicles; plasma; proteomics; small extracellular vesicles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest
Figures
References
-
- Harms A.S., Thome A.D., Yan Z., Schonhoff A.M., Williams G.P., Li X., Liu Y., Qin H., Benveniste E.N., Standaert D.G. Peripheral monocyte entry is required for alpha-Synuclein induced inflammation and Neurodegeneration in a model of Parkinson disease. Exp. Neurol. 2018;300:179–187. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2017.11.010. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

