Comparison of the Diagnostic Efficiency of Radial- and Convex-Arrayed Echoendoscopes for Indirect Findings of Pancreatic Cancer: A Retrospective Comparative Study Using Propensity Score Method
- PMID: 33799500
- PMCID: PMC8001660
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers13061217
Comparison of the Diagnostic Efficiency of Radial- and Convex-Arrayed Echoendoscopes for Indirect Findings of Pancreatic Cancer: A Retrospective Comparative Study Using Propensity Score Method
Abstract
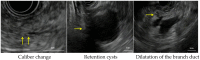
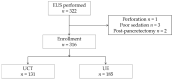
Endoscopic ultrasonography (EUS) is useful for detecting early-stage pancreatic cancer. Because the detection of small lesions is difficult, it is important to detect indirect findings, namely caliber change, retention cysts, and dilatation of the branch duct, during the procedure. Although two types of EUS endoscopes are frequently used, there is no comparative study on their efficacy for detecting indirect findings. Therefore, we aimed to compare the diagnostic efficacy of these two types for indirect findings. We retrospectively analyzed 316 consecutive patients who had undergone EUS for pancreaticobiliary disease at a single center between January 2017 and December 2018. The main outcome was the detection rate of indirect findings and its comparison between the two echoendoscope types. This outcome was achieved using the inverse probability of treatment weighting (IPTW) analysis. The detection rate of indirect findings was higher for the radial-arrayed endoscope than for the convex-arrayed echoendoscope (9.2% vs. 2.3% (p = 0.02)). The univariate analysis also revealed that the radial-arrayed echoendoscope was significantly superior to the convex-arrayed echoendoscope in terms of the detection of indirect findings (odds ratio, 5.94; 95% confidence interval, 1.68-21.10; p = 0.01) after IPTW. After adjustment for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomography (CT), radial-arrayed echoendoscope remained an independent factor for indirect finding detection (odds ratio, 6.04; 95% confidence interval, 1.74-21.00; p = 0.01). Finally, five patients who had indirect EUS findings were diagnosed with pancreatic cancer. Our results indicate that the radial-arrayed echoendoscope is useful for the detection of indirect findings.
Keywords: endoscopic ultrasonography; indirect findings; inverse probability of treatment weighting analysis; pancreatic cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Canto M.I., Hruban R.H., Fishman E.K., Kamel I.R., Schulick R., Zhang Z., Topazian M., Takahashi N., Fletcher J., Petersen G., et al. Frequent detection of pancreatic lesions in asymptomatic high-risk individuals. Gastroenterology. 2012;142:796–804. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2012.01.005. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

