Lean Six Sigma Approach for Reducing Length of Hospital Stay for Patients with Femur Fracture in a University Hospital
- PMID: 33799518
- PMCID: PMC8000325
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph18062843
Lean Six Sigma Approach for Reducing Length of Hospital Stay for Patients with Femur Fracture in a University Hospital
Abstract
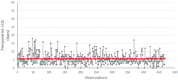
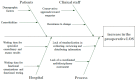
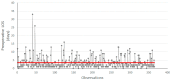
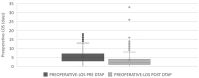
Surgical intervention within 48 h of hospital admission is the gold standard procedure for the management of elderly patients with femur fractures, since the increase in preoperative waiting time is correlated with the onset of complications and longer overall length of stay (LOS) in the hospital. However, national evidence demonstrates that there is still the need to provide timely intervention for this type of patient, especially in some regions of central southern Italy. Here we discuss the introduction of a diagnostic-therapeutic assistance pathway (DTAP) to reduce the preoperative LOS for patients undergoing femur fracture surgery in a university hospital. A Lean Six Sigma methodology, based on the DMAIC cycle (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control), is implemented to evaluate the effectiveness of the DTAP. Data were retrospectively collected and analyzed from two groups of patients before and after the implementation of DTAP over a period of 10 years. The statistics of the process measured before the DTAP showed an average preoperative LOS of 5.6 days (standard deviation of 3.2), thus confirming the need for corrective actions to reduce the LOS in compliance with the national guidelines. The influence of demographic and anamnestic variables on the LOS was evaluated, and the impact of the DTAP was measured and discussed, demonstrating the effectiveness of the improvement actions implemented over the years and leading to a significant reduction in the preoperative LOS, which decreased to an average of 3.5 days (standard deviation of 3.60). The obtained reduction of 39% in the average LOS proved to be in good agreement with previously developed DTAPs for femur fracture available in the literature.
Keywords: Lean Six Sigma; healthcare quality; length of stay; process improvement; public health.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Improving performances of the knee replacement surgery process by applying DMAIC principles.J Eval Clin Pract. 2017 Dec;23(6):1401-1407. doi: 10.1111/jep.12810. Epub 2017 Sep 26. J Eval Clin Pract. 2017. PMID: 28948662 Free PMC article.
-
Use of the Smart Lean Method to Conduct High-Quality Integrated Perioperative Management Prior to Hospitalization.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Dec 20;18(24):13391. doi: 10.3390/ijerph182413391. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34949000 Free PMC article.
-
Six sigma approach for neonatal jaundice patients in an Indian rural hospital - a case study.Int J Health Care Qual Assur. 2019 Dec 17;ahead-of-print(ahead-of-print). doi: 10.1108/IJHCQA-07-2019-0135. Int J Health Care Qual Assur. 2019. PMID: 31886954
-
Effectiveness of dexmedetomidine versus propofol on extubation times, length of stay and mortality rates in adult cardiac surgery patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis.JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2018 May;16(5):1220-1239. doi: 10.11124/JBISRIR-2017-003488. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2018. PMID: 29762314
-
Integrating DMAIC approach of Lean Six Sigma and theory of constraints toward quality improvement in healthcare.Rev Environ Health. 2019 Dec 18;34(4):427-434. doi: 10.1515/reveh-2019-0003. Rev Environ Health. 2019. PMID: 31314742 Review.
Cited by
-
Predictive Analysis of Healthcare-Associated Blood Stream Infections in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit Using Artificial Intelligence: A Single Center Study.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Feb 22;19(5):2498. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19052498. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35270190 Free PMC article.
-
Machine Learning and Regression Analysis to Model the Length of Hospital Stay in Patients with Femur Fracture.Bioengineering (Basel). 2022 Apr 14;9(4):172. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering9040172. Bioengineering (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35447732 Free PMC article.
-
DMAIC methodology for achieving public satisfaction with health departments in various districts of Punjab and optimizing CT scan patient load in urban city hospitals.AIMS Public Health. 2022 May 10;9(2):440-457. doi: 10.3934/publichealth.2022030. eCollection 2022. AIMS Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35634027 Free PMC article.
-
The classification algorithms to support the management of the patient with femur fracture.BMC Med Res Methodol. 2024 Jul 16;24(1):150. doi: 10.1186/s12874-024-02276-5. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2024. PMID: 39014322 Free PMC article.
-
Lean Six Sigma Approach to Improve the Management of Patients Undergoing Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy.Healthcare (Basel). 2024 Jan 23;12(3):292. doi: 10.3390/healthcare12030292. Healthcare (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38338177 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

