Anti-Apoptotic and Anti-Inflammatory Role of Trans ε-Viniferin in a Neuron-Glia Co-Culture Cellular Model of Parkinson's Disease
- PMID: 33799534
- PMCID: PMC7998636
- DOI: 10.3390/foods10030586
Anti-Apoptotic and Anti-Inflammatory Role of Trans ε-Viniferin in a Neuron-Glia Co-Culture Cellular Model of Parkinson's Disease
Abstract
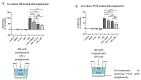
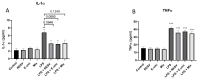
The polyphenol trans-ε-viniferin (viniferin) is a dimer of resveratrol, reported to hold antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. The aims of our study were to evaluate the neuroprotective potential of viniferin in the nerve growth factor (NGF)-differentiated PC12 cells, a dopaminergic cellular model of Parkinson's disease (PD) and assess its anti-inflammatory properties in a N9 microglia-neuronal PC12 cell co-culture system. The neuronal cells were pre-treated with viniferin, resveratrol or their mixture before the administration of 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA), recognized to induce parkinsonism in rats. Furthermore, N9 microglia cells, in a co-culture system with neuronal PC12, were pre-treated with viniferin, resveratrol or their mixture to investigate whether these polyphenols could reduce lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced inflammation. Our results show that viniferin as well as a mixture of viniferin and resveratrol protects neuronal dopaminergic cells from 6-OHDA-induced cytotoxicity and apoptosis. Furthermore, when viniferin, resveratrol or their mixture was used to pre-treat microglia cells in our co-culture system, they reduced neuronal cytotoxicity induced by glial activation. Altogether, our data highlight a novel role for viniferin as a neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory molecule in a dopaminergic cellular model, paving the way for nutraceutical therapeutic avenues in the complementary treatments of PD.
Keywords: Parkinson’s disease; apotosis; dopamine; neuroinflammation; neuroprotection; oxidative stress; resveratrol; trans-ε-viniferin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Neuroprotective mechanisms of ε-viniferin in a rotenone-induced cell model of Parkinson's disease: significance of SIRT3-mediated FOXO3 deacetylation.Neural Regen Res. 2020 Nov;15(11):2143-2153. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.282264. Neural Regen Res. 2020. PMID: 32394973 Free PMC article.
-
Combination of Trans-Resveratrol and ε-Viniferin Induces a Hepatoprotective Effect in Rats with Severe Acute Liver Failure via Reduction of Oxidative Stress and MMP-9 Expression.Nutrients. 2021 Oct 20;13(11):3677. doi: 10.3390/nu13113677. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 34835933 Free PMC article.
-
Resveratrol and quercetin, two natural polyphenols, reduce apoptotic neuronal cell death induced by neuroinflammation.J Neurosci Res. 2008 Feb 1;86(2):403-10. doi: 10.1002/jnr.21503. J Neurosci Res. 2008. PMID: 17929310
-
In the shadow of resveratrol: biological activities of epsilon-viniferin.J Physiol Biochem. 2022 May;78(2):465-484. doi: 10.1007/s13105-022-00880-x. Epub 2022 Mar 21. J Physiol Biochem. 2022. PMID: 35312966 Review.
-
Beneficial Effects of ε-Viniferin on Obesity and Related Health Alterations.Nutrients. 2023 Feb 12;15(4):928. doi: 10.3390/nu15040928. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 36839286 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of Small-Molecule Bioactive Constituents from the Leaves of Vaccinium bracteatum Confirms It as a Potential Functional Food with Health Benefits.Foods. 2023 Jan 1;12(1):177. doi: 10.3390/foods12010177. Foods. 2023. PMID: 36613392 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Neurological Disorders with Stilbenes: Bridging the Preclinical-Clinical Gap.Int J Biol Sci. 2024 Oct 7;20(14):5474-5494. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.102032. eCollection 2024. Int J Biol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39494329 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dim Blue Light at Night Induces Spatial Memory Impairment in Mice by Hippocampal Neuroinflammation and Oxidative Stress.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Jun 22;11(7):1218. doi: 10.3390/antiox11071218. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35883709 Free PMC article.
-
Food Bioactives: Impact on Brain and Cardiometabolic Health-Findings from In Vitro to Human Studies.Foods. 2021 May 11;10(5):1045. doi: 10.3390/foods10051045. Foods. 2021. PMID: 34064632 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of Alnus incana (L.) Moench extracts in ameliorating iron overload-induced hepatotoxicity in male albino rats.Sci Rep. 2023 May 11;13(1):7635. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-34480-6. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37169909 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cohen G. Oxy-radical toxicity in catecholamine neurons. Neurotoxicology. 1984;5:77–82. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

