Kaempferia parviflora Extract Alleviated Rat Arthritis, Exerted Chondroprotective Properties In Vitro, and Reduced Expression of Genes Associated with Inflammatory Arthritis
- PMID: 33799537
- PMCID: PMC8000004
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26061527
Kaempferia parviflora Extract Alleviated Rat Arthritis, Exerted Chondroprotective Properties In Vitro, and Reduced Expression of Genes Associated with Inflammatory Arthritis
Abstract
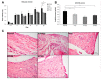
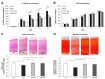
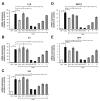
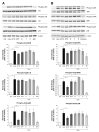
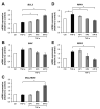
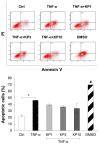
Kaempferia parviflora Wall. ex Baker (KP) has been reported to attenuate cartilage destruction in rat model of osteoarthritis. Previously, we demonstrated that KP rhizome extract and its active components effectively suppressed mechanisms associated with RA in SW982 cells. Here, we further evaluated the anti-arthritis potential of KP extract by using multi-level models, including a complete Freund's adjuvant-induced arthritis and a cartilage explant culture model, and to investigate the effects of KP extract and its major components on related gene expressions and underlying mechanisms within cells. In arthritis rats, the KP extract reduced arthritis indexes, with no significant changes in biological parameters. In the cartilage explant model, the KP extract exerted chondroprotective potential by suppressing sulfated glycosaminoglycans release while preserving high accumulation of proteoglycans. In human chondrocyte cell line, a mixture of the major components equal to their amounts in KP extract showed strong suppression the expression of genes-associated inflammatory joint disease similar to that of the extract. Additionally, KP extract significantly suppressed NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways. The suppressing expression of necroptosis genes and promoted anti-apoptosis were also found. Collectively, these results provided supportive evidence of the anti-arthritis properties of KP extract, which are associated with its three major components.
Keywords: Kaempferia parviflora; anti-arthritis; anti-inflammation; chondroprotection; inflammatory joint disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
-
- Woetzel D., Huber R., Kupfer P., Pohlers D., Pfaff M., Driesch D., Häupl T., Koczan D., Stiehl P., Guthke R., et al. Identification of rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis patients by transcriptome-based rule set generation. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2014;16:R84. doi: 10.1186/ar4526. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

