Emissivity of Building Materials for Infrared Measurements
- PMID: 33799589
- PMCID: PMC8002048
- DOI: 10.3390/s21061961
Emissivity of Building Materials for Infrared Measurements
Abstract
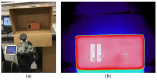
Infrared thermography (IRT) is a technique increasingly used in building inspection. If in many applications it is sufficient to analyze the thermal patterns, others exist in which the exact determination of the surface temperature is a fundamental aspect. In these circumstances, the emissivity of the surfaces assumes special relevance, being probably the most important property in the definition of the boundary conditions. However, information on the uncertainty involved in its measurement, as well as the conditions that influence it, is scarce. This article presents an innovative contribution both to the characterization of the emissivity of various construction materials, and to the discussion of emissivity measurement procedures and the attendant uncertainty. In this sense, three experimental campaigns were carried out: T.I, preliminary tests to assess the initial conditions required for an accurate IRT measurement of the emissivity (reference tape and position of the camera); T.II, assessment of the emissivity of nine different building materials, in dry conditions, using the emissometer and the IRT and black tape methods; and T.III, assessment of the emissivity of three materials during the drying process. The results confirmed that emissivity is a crucial parameter for the accurate measurement of surface temperature. Emissivity measurements carried out with IRT (black tape method) and with the emissometer returned meaningful differences when compared with the values available in the literature. This disagreement led to surface temperature differences of up to 7 °C (emissometer versus reference values). This research also highlighted that the moisture content of the materials influences the emissivity values, with fluctuations that can be greater than 10%, and that the effect of moisture is visible even for low values of moisture content.
Keywords: black tape method; emissivity; emissometer; infrared thermography; moisture content; test procedures.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Balaras C.A., Argiriou A.A. Infrared thermography for building diagnostics. Energy Build. 2002;34:171–183. doi: 10.1016/S0378-7788(01)00105-0. - DOI
-
- Ocaña S., Guerrero I., Requena I. Thermographic survey of two rural buildings in Spain. Energy Build. 2004;36:515–523. doi: 10.1016/j.enbuild.2003.12.012. - DOI
-
- Lerma C., Barreira E., Almeida R.M.S.F. A discussion concerning active infrared thermography in the evaluation of buildings air infiltration. Energy Build. 2018;168:56–66. doi: 10.1016/j.enbuild.2018.02.050. - DOI
-
- Avdelidis N., Moropoulou A., Theoulakis P. Detection of water deposits and movement in porous materials by infrared imaging. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2003;44:183–190. doi: 10.1016/S1350-4495(02)00212-8. - DOI
-
- Grinzato B., Cadelano G., Bison P. Moisture map by IR thermography. J. Mod. Opt. 2010;57:1770–1778. doi: 10.1080/09500341003731597. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

