Chrysin Derivative CM1 and Exhibited Anti-Inflammatory Action by Upregulating Toll-Interacting Protein Expression in Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated RAW264.7 Macrophage Cells
- PMID: 33799689
- PMCID: PMC8000858
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26061532
Chrysin Derivative CM1 and Exhibited Anti-Inflammatory Action by Upregulating Toll-Interacting Protein Expression in Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated RAW264.7 Macrophage Cells
Abstract
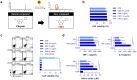
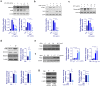
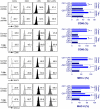
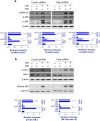
Although our previous study revealed that gamma-irradiated chrysin enhanced anti-inflammatory activity compared to intact chrysin, it remains unclear whether the chrysin derivative, CM1, produced by gamma irradiation, negatively regulates toll-like receptor (TLR) signaling. In this study, we investigated the molecular basis for the downregulation of TLR4 signal transduction by CM1 in macrophages. We initially determined the appropriate concentration of CM1 and found no cellular toxicity below 2 μg/mL. Upon stimulation with lipopolysaccharide (LPS), CM1 modulated LPS-stimulated inflammatory action by suppressing the release of proinflammatory mediators (cytokines TNF-α and IL-6) and nitric oxide (NO) and downregulated the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) signaling pathways. Furthermore, CM1 markedly elevated the expression of the TLR negative regulator toll-interacting protein (Tollip) in dose- and time-dependent manners. LPS-induced expression of cell surface molecules (CD80, CD86, and MHC class I/II), proinflammatory cytokines (TNF-α and IL-6), COX-2, and iNOS-mediated NO were inhibited by CM1; these effects were prevented by the knockdown of Tollip expression. Additionally, CM1 did not affect the downregulation of LPS-induced expression of MAPKs and NF-κB signaling in Tollip-downregulated cells. These findings provide insight into effective therapeutic intervention of inflammatory disease by increasing the understanding of the negative regulation of TLR signaling induced by CM1.
Keywords: anti-inflammatory activity; chrysin derivative; macrophage; toll-interacting protein; toll-like receptor negative regulator.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

