Antagonistic Activity of Bacteria Isolated from the Periplaneta americana L. Gut against Some Multidrug-Resistant Human Pathogens
- PMID: 33799712
- PMCID: PMC7999104
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics10030294
Antagonistic Activity of Bacteria Isolated from the Periplaneta americana L. Gut against Some Multidrug-Resistant Human Pathogens
Abstract
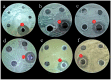
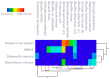
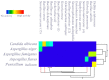
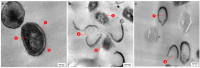
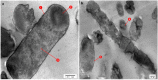
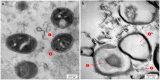
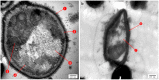
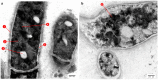
The insect gut is home to a wide range of microorganisms, including several bacterial species. Such bacterial symbionts provide various benefits to their insect hosts. One of such services is providing metabolites that resist infections. Little data are available about gut-inhabiting bacteria for several insect groups. Through the present work, the gut bacteria associated with the American cockroach (Periplaneta americana L.) were isolated, identified, and studied for their potential antimicrobial activity against multidrug-resistant (MDR) human pathogens. The cockroaches were collected from three different environmental sites. Gut bacteria were isolated, and sixteen species of bacteria were identified using Vitek MALDI-TOF MS. The antagonistic activity of the identified bacteria was tested against a panel of multidrug-resistant bacteria and fungi, namely: methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) (clinical isolate), Streptococcus mutans Clarke (RCMB 017(1) ATCC ® 25175™) (Gram-positive bacteria), Enterobacter cloacae (RCMB 001(1) ATCC® 23355™) and Salmonella enterica (ATCC® 25566™) (Gram-negative bacteria). The isolates were also tested against human pathogenic fungi such as Candida albicans (RCMB005003(1) ATCC® 10231™), Aspergillus niger (RCMB002005), Aspergillus fumigatus (RCMB002008), Aspergillus flavus (RCMB002002), and Penicillium italicum (RCMB 001018(1) IMI193019). The results indicated that some bacterial species from the cockroach gut could antagonize the growth activity of all the tested pathogens. Such antimicrobial properties could ultimately lead to the future development of therapeutic drugs. The evaluation and mode of action of antagonistic gut bacteria against the most affected MDR pathogens were demonstrated using transmission electron microscopy (TEM).
Keywords: Cockroaches; antimicrobial; multidrug-resistant (MDR); transmission electron microscope (TEM).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of antimicrobial activity of bacterial symbionts isolated from wild field cockroach Blattella vaga from Saudi Arabia.Saudi J Biol Sci. 2021 Nov;28(11):6239-6244. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2021.06.092. Epub 2021 Jul 3. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34759743 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro evaluation of new 2-phenoxy-benzo[g][1,2,4]triazolo[1,5-a]quinazoline derivatives as antimicrobial agents.Microb Pathog. 2018 Apr;117:60-67. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2018.02.018. Epub 2018 Feb 9. Microb Pathog. 2018. PMID: 29432912
-
Antimicrobial Activity of Synthesized 2-Methylthiobenzo[g][1,2,4]- triazolo[1,5-a]quinazoline Derivatives.Med Chem. 2016;12(8):760-766. doi: 10.2174/1573406412666160502155106. Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 27140181
-
Gut bacteria of cockroaches are a potential source of antibacterial compound(s).Lett Appl Microbiol. 2018 May;66(5):416-426. doi: 10.1111/lam.12867. Epub 2018 Mar 25. Lett Appl Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29457249
-
Bacteria associated with cockroaches: health risk or biotechnological opportunity?Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020 Dec;104(24):10369-10387. doi: 10.1007/s00253-020-10973-6. Epub 2020 Oct 31. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 33128616 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Isolation, Identification, and Biocontrol Potential of Entomopathogenic Nematodes and Associated Bacteria against Virachola livia (Lepidoptera: Lycaenidae) and Ectomyelois ceratoniae (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae).Biology (Basel). 2022 Feb 11;11(2):295. doi: 10.3390/biology11020295. Biology (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35205161 Free PMC article.
-
Microbiome Analysis of Area in Proximity to White Spot Lesions Reveals More Harmful Plant Pathogens in Maize.Biomolecules. 2025 Feb 9;15(2):252. doi: 10.3390/biom15020252. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40001555 Free PMC article.
-
Social wasp-associated Tsukamurella sp. strains showed promising biosynthetic and bioactive potential for discovery of novel compounds.Sci Rep. 2024 Sep 10;14(1):21118. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-71969-0. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39256493 Free PMC article.
-
The potency of herbal extracts and its green synthesized nanoparticle formulation as antibacterial agents against Streptococcus mutans associated biofilms.Biotechnol Rep (Amst). 2022 Dec 11;37:e00777. doi: 10.1016/j.btre.2022.e00777. eCollection 2023 Mar. Biotechnol Rep (Amst). 2022. PMID: 36582762 Free PMC article.
-
Antifungal activity of compounds from Gordonia sp. WA8-44 isolated from the gut of Periplaneta americana and molecular docking studies.Heliyon. 2023 Jul 4;9(7):e17777. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e17777. eCollection 2023 Jul. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37539250 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Odonkor S.T., Addo K.K. Bacteria resistance to antibiotics: Recent trends and challenges. Int. J. Biol. Med. Res. 2011;2:1204–1210.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

