Histamine, Metabolic Remodelling and Angiogenesis: A Systems Level Approach
- PMID: 33799732
- PMCID: PMC8000605
- DOI: 10.3390/biom11030415
Histamine, Metabolic Remodelling and Angiogenesis: A Systems Level Approach
Abstract
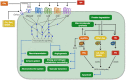
Histamine is a highly pleiotropic biogenic amine involved in key physiological processes including neurotransmission, immune response, nutrition, and cell growth and differentiation. Its effects, sometimes contradictory, are mediated by at least four different G-protein coupled receptors, which expression and signalling pathways are tissue-specific. Histamine metabolism conforms a very complex network that connect many metabolic processes important for homeostasis, including nitrogen and energy metabolism. This review brings together and analyses the current information on the relationships of the "histamine system" with other important metabolic modules in human physiology, aiming to bridge current information gaps. In this regard, the molecular characterization of the role of histamine in the modulation of angiogenesis-mediated processes, such as cancer, makes a promising research field for future biomedical advances.
Keywords: angiogenesis; metabolic remodelling; systems biology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Stark H., editor. Histamine H 4 Receptor: A Novel Drug Target for Immunoregulation and Inflammation. Versita; Berlin, Germany: 2013.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

