Theoretical Determination of High-Energy Photon Attenuation and Recommended Protective Filler Contents for Flexible and Enhanced Dimensionally Stable Wood/NR and NR Composites
- PMID: 33799832
- PMCID: PMC7998293
- DOI: 10.3390/polym13060869
Theoretical Determination of High-Energy Photon Attenuation and Recommended Protective Filler Contents for Flexible and Enhanced Dimensionally Stable Wood/NR and NR Composites
Abstract
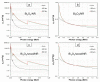
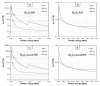
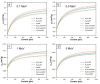
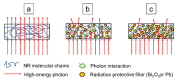
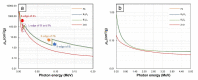
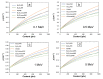
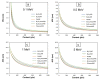
This work aimed to theoretically determine the high-energy-photon-shielding properties of flexible wood/natural rubber (NR) and NR composites containing photon protective fillers, namely Pb, Bi2O3, or Bi2S3, using XCOM. The properties investigated were the mass attenuation coefficient (µm), linear attenuation coefficient (µ), and half value layer (HVL) of the composites, determined at varying photon energies of 0.001-5 MeV and varying filler contents of 0-1000 parts per hundred parts of rubber by weight (phr). The simulated results, which were in good agreement with previously reported experimental values (average difference was 5.3%), indicated that overall shielding properties increased with increasing filler contents but decreased with increasing incident photon energies. The results implied the potential of bismuth compounds, especially Bi2O3, to replace effective but highly toxic Pb as a safer high-energy-photon protective filler, evidenced by just a slight reduction in µm values compared with Pb fillers at the same filler content and photon energy. Furthermore, the results suggested that the addition of 20 phr wood particles, primarily aimed to enhance the rigidity and dimensional stability of Pb/NR, Bi2O3/NR, and Bi2S3/NR composites, did not greatly reduce shielding abilities; hence, they could be used as dimensional reinforcers for NR composites. Lastly, this work also reported the optimum Pb, Bi2O3, or Bi2S3 contents in NR and wood/NR composites at photon energies of 0.1, 0.5, 1, and 5 MeV, with 316-624 phr of filler being the recommended contents, of which the values depended on filler type and photon energy of interest.
Keywords: Bi2O3; Bi2S3; Pb; X-ray; XCOM; gamma; natural rubber; photon; shielding; wood particles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Rare-Earth Oxides as Alternative High-Energy Photon Protective Fillers in HDPE Composites: Theoretical Aspects.Polymers (Basel). 2021 Jun 10;13(12):1930. doi: 10.3390/polym13121930. Polymers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34200711 Free PMC article.
-
High-Energy Photon Attenuation Properties of Lead-Free and Self-Healing Poly (Vinyl Alcohol) (PVA) Hydrogels: Numerical Determination and Simulation.Gels. 2022 Mar 22;8(4):197. doi: 10.3390/gels8040197. Gels. 2022. PMID: 35448098 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative X-ray Shielding Properties of Single-Layered and Multi-Layered Bi2O3/NR Composites: Simulation and Numerical Studies.Polymers (Basel). 2022 Apr 27;14(9):1788. doi: 10.3390/polym14091788. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35566961 Free PMC article.
-
Research Progress of Natural Rubber Wet Mixing Technology.Polymers (Basel). 2024 Jul 2;16(13):1899. doi: 10.3390/polym16131899. Polymers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39000755 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Shielding characteristics of nanocomposites for protection against X- and gamma rays in medical applications: effect of particle size, photon energy and nano-particle concentration.Radiat Environ Biophys. 2020 Nov;59(4):583-600. doi: 10.1007/s00411-020-00865-8. Epub 2020 Aug 11. Radiat Environ Biophys. 2020. PMID: 32780196 Review.
Cited by
-
Rare-Earth Oxides as Alternative High-Energy Photon Protective Fillers in HDPE Composites: Theoretical Aspects.Polymers (Basel). 2021 Jun 10;13(12):1930. doi: 10.3390/polym13121930. Polymers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34200711 Free PMC article.
-
High-Energy Photon Attenuation Properties of Lead-Free and Self-Healing Poly (Vinyl Alcohol) (PVA) Hydrogels: Numerical Determination and Simulation.Gels. 2022 Mar 22;8(4):197. doi: 10.3390/gels8040197. Gels. 2022. PMID: 35448098 Free PMC article.
-
X-ray Shielding, Mechanical, Physical, and Water Absorption Properties of Wood/PVC Composites Containing Bismuth Oxide.Polymers (Basel). 2021 Jul 4;13(13):2212. doi: 10.3390/polym13132212. Polymers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34279356 Free PMC article.
-
A Comparative Study on X-ray Shielding and Mechanical Properties of Natural Rubber Latex Nanocomposites Containing Bi2O3 or BaSO4: Experimental and Numerical Determination.Polymers (Basel). 2022 Sep 2;14(17):3654. doi: 10.3390/polym14173654. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36080729 Free PMC article.
-
Experimental Investigation of X-Ray Radiation Shielding and Radiological Properties for Various Natural Composites.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2023 Oct 1;24(10):3555-3561. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2023.24.10.3555. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2023. PMID: 37898863 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sakdinawat A., Attwood D. Nanoscale X-ray imaging. Nat. Photon. 2010;4:840–848. doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2010.267. - DOI
-
- Smeets J., Roellinghoff F., Prieels D., Stichelbaut F., Benilov A., Busca P., Fiorini C., Peloso R., Basilavecchia M., Frizzi T., et al. Prompt gamma imaging with a slit camera for real-time range control in proton therapy. Phys. Med. Biol. 2012;57:3371–3405. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/57/11/3371. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Fan F., Gao S., Ji S., Fu Y., Zhang P., Xu H. Gamma radiation-responsive side-chain tellurium-containing polymer for cancer therapy. Mater. Chem. Front. 2018;2:2109–2115. doi: 10.1039/C8QM00321A. - DOI
-
- Shin J.M., Kim B.K., Seol S.G., Jeon S.B., Kim J.S., Jun B.K., Kang S.Y., Lee J.S., Chung M.N., Kim S.H. Mutation breeding of sweet potato by gamma-ray radiation. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2011;6:1447–1454.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

