microRNA-mRNA Profile of Skeletal Muscle Differentiation and Relevance to Congenital Myotonic Dystrophy
- PMID: 33799993
- PMCID: PMC7962092
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22052692
microRNA-mRNA Profile of Skeletal Muscle Differentiation and Relevance to Congenital Myotonic Dystrophy
Abstract
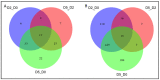
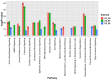
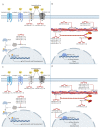
microRNAs (miRNAs) regulate messenger RNA (mRNA) abundance and translation during key developmental processes including muscle differentiation. Assessment of miRNA targets can provide insight into muscle biology and gene expression profiles altered by disease. mRNA and miRNA libraries were generated from C2C12 myoblasts during differentiation, and predicted miRNA targets were identified based on presence of miRNA binding sites and reciprocal expression. Seventeen miRNAs were differentially expressed at all time intervals (comparing days 0, 2, and 5) of differentiation. mRNA targets of differentially expressed miRNAs were enriched for functions related to calcium signaling and sarcomere formation. To evaluate this relationship in a disease state, we evaluated the miRNAs differentially expressed in human congenital myotonic dystrophy (CMD) myoblasts and compared with normal control. Seventy-four miRNAs were differentially expressed during healthy human myocyte maturation, of which only 12 were also up- or downregulated in CMD patient cells. The 62 miRNAs that were only differentially expressed in healthy cells were compared with differentiating C2C12 cells. Eighteen of the 62 were conserved in mouse and up- or down-regulated during mouse myoblast differentiation, and their C2C12 targets were enriched for functions related to muscle differentiation and contraction.
Keywords: congenital myotonic dystrophy; microRNA; muscle differentiation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Kim E., Cook-Mills J., Morgan G., Sredni S.T., Pachman L.M. Increased expression of vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 in muscle biopsy samples from juvenile dermatomyositis patients with short duration of untreated disease is regulated by miR-126. Arthritis Rheum. 2012;64:3809–3817. doi: 10.1002/art.34606. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Karolina D.S., Armugam A., Tavintharan S., Wong M.T.K., Lim S.C., Sum C.F., Jeyaseelan K. MicroRNA 144 Impairs Insulin Signaling by Inhibiting the Expression of Insulin Receptor Substrate 1 in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. PLoS ONE. 2011;6:e22839. doi: 10.1371/annotation/698b7123-174f-4a09-95c9-fd6f5017d622. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

