The Administration of the Synbiotic Lactobacillus bulgaricus 6c3 Strain, Inulin and Fructooligosaccharide Decreases the Concentrations of Indoxyl Sulfate and Kidney Damage in a Rat Model
- PMID: 33800029
- PMCID: PMC7999732
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins13030192
The Administration of the Synbiotic Lactobacillus bulgaricus 6c3 Strain, Inulin and Fructooligosaccharide Decreases the Concentrations of Indoxyl Sulfate and Kidney Damage in a Rat Model
Abstract
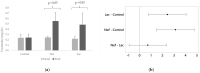
Indoxyl sulfate (IS) is involved in the progression of chronic kidney disease (CKD) and in its cardiovascular complications. One of the approaches proposed to decrease IS is the administration of synbiotics. This work aimed to search for a probiotic strain capable to decrease serum IS levels and mix it with two prebiotics (inulin and fructooligosaccharide (FOS)) to produce a putative synbiotic and test it in a rat CKD model. Two groups of Sprague-Dawley rats were nephrectomized. One group (Lac) received the mixture for 16 weeks in drinking water and the other no (Nef). A control group (C) included sham-nephrectomized rats. Serum creatinine and IS concentrations were measured using high-performance liquid chromatography with diode array detector (HPLC-DAD). Optical microscopy and two-photon excitation microscopy was used to study kidney and heart samples. The Lac group, which received the synbiotic, reduced IS by 0.8% while the Nef group increased it by 38.8%. Histological analysis of kidneys showed that the Lac group increased fibrotic areas by 12% and the Nef group did it by 25%. The synbiotic did not reduce cardiac fibrosis. Therefore, the putative synbiotic showed that function reducing IS and the progression of CKD in a rat model, but no heart protection was observed.
Keywords: CKD; CVD; indoxyl sulfate; renal fibrosis; synbiotic.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Effects of prebiotic oligofructose-enriched inulin on gut-derived uremic toxins and disease progression in rats with adenine-induced chronic kidney disease.PLoS One. 2021 Oct 6;16(10):e0258145. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0258145. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34614017 Free PMC article.
-
An Innovative Synbiotic Formulation Decreases Free Serum Indoxyl Sulfate, Small Intestine Permeability and Ameliorates Gastrointestinal Symptoms in a Randomized Pilot Trial in Stage IIIb-IV CKD Patients.Toxins (Basel). 2021 May 5;13(5):334. doi: 10.3390/toxins13050334. Toxins (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34063068 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The Impact of Synbiotic Treatment on the Levels of Gut-Derived Uremic Toxins, Inflammation, and Gut Microbiome of Chronic Kidney Disease Patients-A Randomized Trial.J Ren Nutr. 2023 Mar;33(2):278-288. doi: 10.1053/j.jrn.2022.07.008. Epub 2022 Aug 19. J Ren Nutr. 2023. PMID: 35995418 Clinical Trial.
-
Prebiotic, Probiotic, and Synbiotic Supplementation in Chronic Kidney Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.J Ren Nutr. 2019 May;29(3):209-220. doi: 10.1053/j.jrn.2018.08.008. Epub 2018 Oct 23. J Ren Nutr. 2019. PMID: 30366767
-
Protein-bound uremic toxin lowering strategies in chronic kidney disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Nephrol. 2021 Dec;34(6):1805-1817. doi: 10.1007/s40620-020-00955-2. Epub 2021 Jan 23. J Nephrol. 2021. PMID: 33484425
Cited by
-
Pathogenesis of Sarcopenia in Chronic Kidney Disease-The Role of Inflammation, Metabolic Dysregulation, Gut Dysbiosis, and microRNA.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 3;25(15):8474. doi: 10.3390/ijms25158474. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39126043 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microbial-Derived Tryptophan Catabolites, Kidney Disease and Gut Inflammation.Toxins (Basel). 2022 Sep 18;14(9):645. doi: 10.3390/toxins14090645. Toxins (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36136583 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biotics and bacterial function: impact on gut and host health.ISME J. 2024 Jan 8;18(1):wrae226. doi: 10.1093/ismejo/wrae226. ISME J. 2024. PMID: 39499657 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Future of Uremic Toxin Management.Toxins (Basel). 2024 Oct 28;16(11):463. doi: 10.3390/toxins16110463. Toxins (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39591217 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Uremia-Induced Gut Barrier Defect in 5/6 Nephrectomized Mice Is Worsened by Candida Administration through a Synergy of Uremic Toxin, Lipopolysaccharide, and (1➔3)-β-D-Glucan, but Is Attenuated by Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus L34.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 24;23(5):2511. doi: 10.3390/ijms23052511. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35269654 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zoccali C., Vanholder R., Massy Z.A., Ortiz A., Sarafidis P., Dekker F.W., Fliser D., Fouque D., Heine G.H., Jager K.J., et al. Cardiovascular Medicine Working Group of the European Renal Association—European Dialysis Transplantation, A. The systemic nature of CKD. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2017;13:344–358. doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2017.52. - DOI - PubMed
-
- CDC Chronic Kidney Disease in the United States. [(accessed on 8 April 2020)];2019 Available online: Availabe online: https://www.cdc.gov/kidneydisease/pdf/2019_National-Chr....
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

