In Vitro Human Joint Models Combining Advanced 3D Cell Culture and Cutting-Edge 3D Bioprinting Technologies
- PMID: 33800436
- PMCID: PMC7999996
- DOI: 10.3390/cells10030596
In Vitro Human Joint Models Combining Advanced 3D Cell Culture and Cutting-Edge 3D Bioprinting Technologies
Abstract
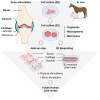
Joint-on-a-chip is a new technology able to replicate the joint functions into microscale systems close to pathophysiological conditions. Recent advances in 3D printing techniques allow the precise control of the architecture of the cellular compartments (including chondrocytes, stromal cells, osteocytes and synoviocytes). These tools integrate fluid circulation, the delivery of growth factors, physical stimulation including oxygen level, external pressure, and mobility. All of these structures must be able to mimic the specific functions of the diarthrodial joint: mobility, biomechanical aspects and cellular interactions. All the elements must be grouped together in space and reorganized in a manner close to the joint organ. This will allow the study of rheumatic disease physiopathology, the development of biomarkers and the screening of new drugs.
Keywords: microspheres; musculoskeletal progenitor/stromal cells; organoids.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cutting-Edge Technologies for Inflamed Joints on Chip: How Close Are We?Front Immunol. 2022 Mar 10;13:802440. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.802440. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35359987 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Consistent and reproducible cultures of large-scale 3D mammary epithelial structures using an accessible bioprinting platform.Breast Cancer Res. 2018 Oct 10;20(1):122. doi: 10.1186/s13058-018-1045-4. Breast Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 30305139 Free PMC article.
-
Towards Single-Step Biofabrication of Organs on a Chip via 3D Printing.Trends Biotechnol. 2016 Sep;34(9):685-688. doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2016.06.005. Epub 2016 Jul 13. Trends Biotechnol. 2016. PMID: 27424152
-
Bioprinting technologies for disease modeling.Biotechnol Lett. 2017 Sep;39(9):1279-1290. doi: 10.1007/s10529-017-2360-z. Epub 2017 May 26. Biotechnol Lett. 2017. PMID: 28550360 Review.
-
Deterministically patterned biomimetic human iPSC-derived hepatic model via rapid 3D bioprinting.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Feb 23;113(8):2206-11. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1524510113. Epub 2016 Feb 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 26858399 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Advances in Engineered Three-Dimensional (3D) Body Articulation Unit Models.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2022 Jan 18;16:213-235. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S344036. eCollection 2022. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2022. PMID: 35087267 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Novel Method Facilitating the Simple and Low-Cost Preparation of Human Osteochondral Slice Explants for Large-Scale Native Tissue Analysis.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 15;22(12):6394. doi: 10.3390/ijms22126394. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34203791 Free PMC article.
-
Organ-on-a-chip technologies for biomedical research and drug development: A focus on the vasculature.Smart Med. 2023 Feb 26;2(1):e20220030. doi: 10.1002/SMMD.20220030. Epub 2023 Feb 24. Smart Med. 2023. PMID: 37089706 Free PMC article.
-
Leveraging whole blood based functional flow cytometry assays to open new perspectives for rheumatoid arthritis translational research.Sci Rep. 2022 Jul 16;12(1):12166. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-16622-4. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35842449 Free PMC article.
-
Organoids as Innovative Models for Bone and Joint Diseases.Cells. 2023 Jun 8;12(12):1590. doi: 10.3390/cells12121590. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37371060 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jain A., Mathur T., Pandian N.K., Selahi A. Precision Medicine for Investigators, Practitioners and Providers. Elsevier BV; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2020. Organ-on-a-chip and 3D printing as preclinical models for medical research and practice; pp. 83–95.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

