Non-Metabolic Functions of PKM2 Contribute to Cervical Cancer Cell Proliferation Induced by the HPV16 E7 Oncoprotein
- PMID: 33800513
- PMCID: PMC8001101
- DOI: 10.3390/v13030433
Non-Metabolic Functions of PKM2 Contribute to Cervical Cancer Cell Proliferation Induced by the HPV16 E7 Oncoprotein
Abstract
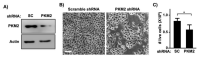
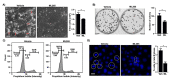
Pyruvate kinase M2 (PKM2) mainly catalyzes glycolysis, but it also exerts non-glycolytic functions in several cancers. While it has been shown to interact with the human papillomavirus 16 (HPV16) E7 oncoprotein, the functional significance of PKM2 in HPV-associated cervical cancer has been elusive. Here, we show that HPV16 E7 increased the expression of PKM2 in cervical cancer cells. TCGA data analyses revealed a higher level of PKM2 in HPV+ than HPV- cervical cancers and a worse prognosis for patients with high PKM2 expression. Functionally, we demonstrate that shRNA-mediated PKM2 knockdown decreased the proliferation of HPV+ SiHa cervical cancer cells. PKM2 knockdown also inhibited the E7-induced proliferation of cervical cancer cells. ML265 activating the pyruvate kinase function of PKM2 inhibited cell cycle progression and colony formation. ML265 treatments decreased phosphorylation of PKM2 at the Y105 position that has been associated with non-glycolytic functions. On the contrary, HPV16 E7 increased the PKM2 phosphorylation. Our results indicate that E7 increases PKM2 expression and activates a non-glycolytic function of PKM2 to promote cervical cancer cell proliferation.
Keywords: HPV16 E7; ML265; PKM2; cervical cancer; non-pyruvate kinase function.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Functions and modulation of PKM2 activity by human papillomavirus E7 oncoprotein (Review).Oncol Lett. 2022 Nov 14;25(1):7. doi: 10.3892/ol.2022.13593. eCollection 2023 Jan. Oncol Lett. 2022. PMID: 36478899 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human papillomavirus 16E6/E7 activates autophagy via Atg9B and LAMP1 in cervical cancer cells.Cancer Med. 2019 Aug;8(9):4404-4416. doi: 10.1002/cam4.2351. Epub 2019 Jun 18. Cancer Med. 2019. PMID: 31215164 Free PMC article.
-
Human Papillomavirus E6/E7 and Long Noncoding RNA TMPOP2 Mutually Upregulated Gene Expression in Cervical Cancer Cells.J Virol. 2019 Apr 3;93(8):e01808-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01808-18. Print 2019 Apr 15. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 30728257 Free PMC article.
-
N6-methyladenosine methylation on FSCN1 mediated by METTL14/IGF2BP3 contributes to human papillomavirus type 16-infected cervical squamous cell carcinoma.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2024 Jun;51(6):e13864. doi: 10.1111/1440-1681.13864. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38679464
-
Cellular Functions of HPV16 E5 Oncoprotein during Oncogenic Transformation.Mol Cancer Res. 2021 Feb;19(2):167-179. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-20-0491. Epub 2020 Oct 26. Mol Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 33106372 Review.
Cited by
-
Apatinib weakens proliferation, migration, invasion, and angiogenesis of thyroid cancer cells through downregulating pyruvate kinase M2.Sci Rep. 2024 Jan 9;14(1):879. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-50369-w. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38195651 Free PMC article.
-
Functions and modulation of PKM2 activity by human papillomavirus E7 oncoprotein (Review).Oncol Lett. 2022 Nov 14;25(1):7. doi: 10.3892/ol.2022.13593. eCollection 2023 Jan. Oncol Lett. 2022. PMID: 36478899 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The potential role of HPV oncoproteins in the PD-L1/PD-1 pathway in cervical cancer: new perspectives on cervical cancer immunotherapy.Front Oncol. 2024 Dec 13;14:1488730. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1488730. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39735605 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phosphorylated PKM2 regulates endothelium-dependent vasodilation in diabetes.Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2023 May 28;48(5):663-670. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2023.220541. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2023. PMID: 37539568 Free PMC article. Chinese, English.
-
Human papillomavirus associated cervical lesion: pathogenesis and therapeutic interventions.MedComm (2020). 2023 Sep 14;4(5):e368. doi: 10.1002/mco2.368. eCollection 2023 Oct. MedComm (2020). 2023. PMID: 37719443 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

