Prognostic Markers for Chorioamnionitis: IL-6, TNF-α, and MMP-8 in Vaginally Obtained Amniotic Fluid
- PMID: 33800521
- PMCID: PMC7962957
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm10051136
Prognostic Markers for Chorioamnionitis: IL-6, TNF-α, and MMP-8 in Vaginally Obtained Amniotic Fluid
Abstract
Background: Earlier chorioamnionitis diagnosis is crucial to improve maternal and neonatal health outcomes. This study was conducted to evaluate the inlerleukin-6 (IL-6), tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α), and matrix metalloproteinase 8 (MMP-8) levels in vaginally obtained amniotic fluid to investigate their prognostic value and to determine the most appropriate cut-off values for the prediction of chorioamnionitis.
Methods: This case control study included women who were diagnosed with preterm premature rupture of the membranes before 34 weeks of gestation and were admitted to Vilnius University Hospital Santaros Klinikos. Free-leaking amniotic fluid was obtained vaginally with a sterile speculum less than 48h before delivery. Amniotic fluid IL-6, TNF-α, and MMP-8 levels were determined by the Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay. Diagnosis of chorioamnionitis was confirmed by histological examination of the placenta and membranes after delivery.
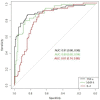
Results: The study included 156 women, 65 patients in the histological chorioamnionitis group (Group I) and 91 in a group without diagnosed histological chorioamnionitis (Group II). The median concentrations of IL-6, MMP-8, and TNF-α in amniotic fluid were statistically significantly higher in Group I than in Group II (p-value < 0.001). The area under the curve of TNF-α and MMP-8 were higher than the area under the curve of IL-6 (0.91, 0.89, and 0.81, respectively). No statistically significant difference was found when comparing the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves of TNF-α and MMP-8. The optimum cut-off values for the prediction of chorioamnionitis were found to be 1389.82 pg/mL for IL-6, 21.17 pg/mL for TNF-α, and 172.53 ng/mL for MMP-8. The sensitivity, specificity, positive prognostic value (PPV), and negative prognostic value (NPV) of the IL-6 cut-off for chorioamnionitis were 88%, 70%, 67%, and 89%, respectively. The sensitivity, specificity, PPV, and NPV of the TNF-α cut-off were 88%, 84%, 79%, and 90%, respectively. The sensitivity, specificity, PPV, and NPV of the MMP-8 cut-off were 80%, 87%, 81%, and 86%, respectively.
Conclusions: The vaginally obtained amniotic fluid IL-6, MMP-8, and TNF-α seem to be good predictors for chorioamnionitis of patients with preterm premature rupture of membranes before 34 weeks of gestation. The noninvasive technique of sampling amniotic fluid could be alternative method to invasive amniocentesis.
Keywords: IL-6; MMP-8; TNF-α; chorioamnionitis; immunological markers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Soluble urokinase plasminogen activator receptor in vaginally collected amniotic fluid predicting fetal inflammatory response syndrome: a prospective cohort study.BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2024 Jan 10;24(1):54. doi: 10.1186/s12884-023-06221-0. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2024. PMID: 38200448 Free PMC article.
-
The significance of TNF-α and MMP-8 concentrations in non-invasively obtained amniotic fluid predicting fetal inflammatory response syndrome.Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2023 Feb;160(2):476-482. doi: 10.1002/ijgo.14478. Epub 2022 Oct 7. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2023. PMID: 36151969 Free PMC article.
-
A value of soluble Toll-like receptor 2 and 4 in vaginally obtained amniotic fluid for the prediction of histological chorioamnionitis.Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2021 Dec;100(12):2209-2215. doi: 10.1111/aogs.14228. Epub 2021 Jul 26. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2021. PMID: 34244993 Free PMC article.
-
Cytokines in noninvasively obtained amniotic fluid as predictors of fetal inflammatory response syndrome.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2016 Jul;215(1):96.e1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2016.01.181. Epub 2016 Jan 29. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2016. PMID: 26829512
-
Early- or mid-trimester amniocentesis biomarkers for predicting preterm delivery: a meta-analysis.Ann Med. 2017 Feb;49(1):1-10. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2016.1211789. Epub 2016 Aug 5. Ann Med. 2017. PMID: 27494609 Review.
Cited by
-
Reference values for interleukin-6 in the amniotic fluid of asymptomatic pregnant women.Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2023 Apr;102(4):480-485. doi: 10.1111/aogs.14524. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2023. PMID: 36906815 Free PMC article.
-
The Significance of Epidermal Growth Factor in Noninvasively Obtained Amniotic Fluid Predicting Respiratory Outcomes of Preterm Neonates.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 10;23(6):2978. doi: 10.3390/ijms23062978. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35328399 Free PMC article.
-
Soluble urokinase plasminogen activator receptor in vaginally collected amniotic fluid predicting fetal inflammatory response syndrome: a prospective cohort study.BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2024 Jan 10;24(1):54. doi: 10.1186/s12884-023-06221-0. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2024. PMID: 38200448 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment strategies for intra-amniotic infection and/or inflammation in preterm labor cases.Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol X. 2025 Jun 8;27:100408. doi: 10.1016/j.eurox.2025.100408. eCollection 2025 Sep. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol X. 2025. PMID: 40607307 Free PMC article.
-
Palmitate and group B Streptococcus synergistically and differentially induce IL-1β from human gestational membranes.Front Immunol. 2024 May 23;15:1409378. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1409378. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38855112 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

