Effect of Training-Detraining Phases of Multicomponent Exercises and BCAA Supplementation on Inflammatory Markers and Albumin Levels in Frail Older Persons
- PMID: 33800577
- PMCID: PMC8066027
- DOI: 10.3390/nu13041106
Effect of Training-Detraining Phases of Multicomponent Exercises and BCAA Supplementation on Inflammatory Markers and Albumin Levels in Frail Older Persons
Abstract
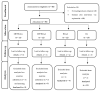
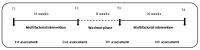
Nowadays, it is accepted that the regular practice of exercise and branched-chain amino acids supplementation (BCAAs) can benefit the immune responses in older persons, prevent the occurrence of physical frailty (PF), cognitive decline, and aging-related comorbidities. However, the impact of their combination (as non-pharmacological interventions) in albumin and the inflammatory markers is not fully understood. Therefore, we investigated the effect of a 40-week multifactorial intervention [MIP, multicomponent exercise (ME) associated or not with BCAAs] on plasma levels of inflammatory markers and albumin in frail older persons (≥75 years old) living at residential care homes (RCH). This study consisted of a prospective, naturalistic, controlled clinical trial with four arms of multifactorial and experimental (interventions-wahshout-interventions) design. The intervention groups were ME + BCAAs (n = 8), ME (n = 7), BCAAs (n = 7), and control group (n = 13). Lower limb muscle-strength, cognitive profile, and PF tests were concomitantly evaluated with plasma levels of albumin, anti- and pro-inflammatory cytokines [Interleukin-10 (IL-10) and Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha (TNF-α) respectively], TNF-α/IL-10 ratio, and myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity at four different time-points: Baseline (T1), after 16 weeks of multifactorial intervention (T2), then after a subsequent 8 weeks washout period (T3) and finally, after an additional 16 weeks of multifactorial intervention (T4). Improvement of cognitive profile and muscle strength-related albumin levels, as well as reduction in the TNF-α levels were found particularly in ME plus BCAAs group. No significant variations were observed over time for TNF-α/IL-10 ratio or MPO activity. Overall, the study showed that MIP triggered slight alterations in the inflammatory and physical function of the frail older participants, which could provide independence and higher quality of life for this population.
Keywords: cognitive impairment; cytokines; inflammaging; physical frailty; protein intake.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Aiello A., Farzaneh F., Candore G., Caruso C., Davinelli S., Gambino C.M., Ligotti M.E., Zareian N., Accardi G. Immunosenescence and its hallmarks: How to oppose aging strategically? A review of potential options for therapeutic intervention. Front. Immunol. 2019;10:1–19. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02247. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Amirato G.R., Borges J.O., Marques D.L., Santos J.M.B., Santos C.A.F., Andrade M.S., Furtado G.E., Rossi M., Luis L.N., Zambonatto R.F., et al. L-glutamine supplementation enhances strength and power of knee muscles and improves glycemia control and plasma redox balance in exercising elderly women. Nutrients. 2021;13:1025. doi: 10.3390/nu13031025. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chodzko-Zajko W., Schwingel A. Successful Aging: The Role of Physical Activity. Am. J. Lifestyle Med. 2008;3:20–28. doi: 10.1177/1559827608325456. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

