Cyclodextrins as Supramolecular Recognition Systems: Applications in the Fabrication of Electrochemical Sensors
- PMID: 33800708
- PMCID: PMC8036645
- DOI: 10.3390/ma14071668
Cyclodextrins as Supramolecular Recognition Systems: Applications in the Fabrication of Electrochemical Sensors
Abstract
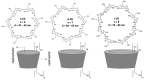
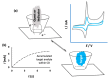
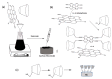
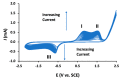
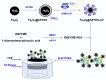
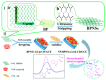
Supramolecular chemistry, although focused mainly on noncovalent intermolecular and intramolecular interactions, which are considerably weaker than covalent interactions, can be employed to fabricate sensors with a remarkable affinity for a target analyte. In this review the development of cyclodextrin-based electrochemical sensors is described and discussed. Following a short introduction to the general properties of cyclodextrins and their ability to form inclusion complexes, the cyclodextrin-based sensors are introduced. This includes the combination of cyclodextrins with reduced graphene oxide, carbon nanotubes, conducting polymers, enzymes and aptamers, and electropolymerized cyclodextrin films. The applications of these materials as chiral recognition agents and biosensors and in the electrochemical detection of environmental contaminants, biomolecules and amino acids, drugs and flavonoids are reviewed and compared. Based on the papers reviewed, it is clear that cyclodextrins are promising molecular recognition agents in the creation of electrochemical sensors, chiral sensors, and biosensors. Moreover, they have been combined with a host of materials to enhance the detection of the target analytes. Nevertheless, challenges remain, including the development of more robust methods for the integration of cyclodextrins into the sensing unit.
Keywords: biosensors; chiral recognition; cyclodextrins; electrochemical sensors; inclusion complex.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures




References
-
- Fox C.M., Breslin C.B. Electrochemical formation of silver nanoparticles and their applications in the reduction and detection of nitrates at neutral pH. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2020;50:125–138. doi: 10.1007/s10800-019-01374-3. - DOI
-
- Windmiller J.R., Wang J. Wearable electrochemical sensors and biosensors: A review. Electroanalysis. 2013;25:29–46. doi: 10.1002/elan.201200349. - DOI
-
- Nasiri S., Khosravani M.R. Progress and challenges in fabrication of wearable sensors for health monitoring. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2020;312 doi: 10.1016/j.sna.2020.112105. - DOI
-
- Mead M.I., Popoola O.A.M., Stewart G.B., Landshoff P., Calleja M., Hayes M., Baldovi J.J., McLeod M.W., Hodgson T.F., Dicks J., et al. The use of electrochemical sensors for monitoring urban air quality in low-cost, high-density networks. Atmos. Environ. 2013;70:186–203. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2012.11.060. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

