Systemic Administration of G-CSF Accelerates Bone Regeneration and Modulates Mobilization of Progenitor Cells in a Rat Model of Distraction Osteogenesis
- PMID: 33800710
- PMCID: PMC8037338
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22073505
Systemic Administration of G-CSF Accelerates Bone Regeneration and Modulates Mobilization of Progenitor Cells in a Rat Model of Distraction Osteogenesis
Abstract
Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) was shown to promote bone regeneration and mobilization of vascular and osteogenic progenitor cells. In this study, we investigated the effects of a systemic low dose of G-CSF on both bone consolidation and mobilization of hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells (HSPCs), endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) and mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) in a rat model of distraction osteogenesis (DO). Neovascularization and mineralization were longitudinally monitored using positron emission tomography and planar scintigraphy. Histological analysis was performed and the number of circulating HSPCs, EPCs and MSCs was studied by flow cytometry. Contrary to control group, in the early phase of consolidation, a bony bridge with lower osteoclast activity and a trend of an increase in osteoblast activity were observed in the distracted callus in the G-CSF group, whereas, at the late phase of consolidation, a significantly lower neovascularization was observed. While no difference was observed in the number of circulating EPCs between control and G-CSF groups, the number of MSCs was significantly lower at the end of the latency phase and that of HSPCs was significantly higher 4 days after the bone lengthening. Our results indicate that G-CSF accelerates bone regeneration and modulates mobilization of progenitor cells during DO.
Keywords: G-CSF; bone formation; endothelial progenitor cells; hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells; mesenchymal stromal cells; neovascularization.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
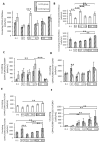
 represents the latency period, the distraction phase is represented by
represents the latency period, the distraction phase is represented by  , and
, and  represents the consolidation phase. ** p < 0.05, *** p < 0.01. Cytometry assays were performed on 6 G-CSF animals and 4 control animals.
represents the consolidation phase. ** p < 0.05, *** p < 0.01. Cytometry assays were performed on 6 G-CSF animals and 4 control animals.
 represents the latency period,
represents the latency period,  represents the distraction phase and the consolidation phase is represented by
represents the distraction phase and the consolidation phase is represented by  . Planar scintigraphy was performed on 6 control animals and 4 G-CSF animals. ** p < 0.05, *** p < 0.01, **** p < 0.001, ***** p < 0.0001.
. Planar scintigraphy was performed on 6 control animals and 4 G-CSF animals. ** p < 0.05, *** p < 0.01, **** p < 0.001, ***** p < 0.0001.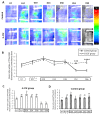
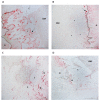
 represent the latency period, the distraction phase is represented by
represent the latency period, the distraction phase is represented by  , and
, and  the consolidation phase. *** p < 0.01, **** p < 0.001.
the consolidation phase. *** p < 0.01, **** p < 0.001.
References
-
- Singh M., Vashistha A., Chaudhary M., Kaur G. Biological Basis of Distraction Osteogenesis—A Review. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. Med. and Pathol. 2016;28 doi: 10.1016/j.ajoms.2015.05.006. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

