The Regulatory Cross-Talk between microRNAs and Novel Members of the B7 Family in Human Diseases: A Scoping Review
- PMID: 33800752
- PMCID: PMC7962059
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22052652
The Regulatory Cross-Talk between microRNAs and Novel Members of the B7 Family in Human Diseases: A Scoping Review
Abstract
The members of the B7 family, as immune checkpoint molecules, can substantially regulate immune responses. Since microRNAs (miRs) can regulate gene expression post-transcriptionally, we conducted a scoping review to summarize and discuss the regulatory cross-talk between miRs and new B7 family immune checkpoint molecules, i.e., B7-H3, B7-H4, B7-H5, butyrophilin like 2 (BTNL2), B7-H6, B7-H7, and immunoglobulin like domain containing receptor 2 (ILDR2). The current study was performed using a six-stage methodology structure and Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guideline. PubMed, Embase, Scopus, Cochrane, ProQuest, and Google Scholar were systematically searched to obtain the relevant records to 5 November 2020. Two authors independently reviewed the obtained records and extracted the desired data. After quantitative and qualitative analyses, we used bioinformatics approaches to extend our knowledge about the regulatory cross-talk between miRs and the abovementioned B7 family members. Twenty-seven articles were identified that fulfilled the inclusion criteria. Studies with different designs reported gene-miR regulatory axes in various cancer and non-cancer diseases. The regulatory cross-talk between the aforementioned B7 family molecules and miRs might provide valuable insights into the pathogenesis of various human diseases.
Keywords: B7; cancer; gene therapy; human diseases; immune checkpoint; immunotherapy; microRNA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
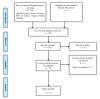

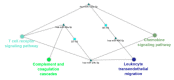
References
-
- Chapoval A.I., Chapoval S.P., Shcherbakova N.S., Shcherbakov D.N. Immune Checkpoints of the B7 Family. Part 2. Representatives of the B7 Family B7-H3, B7-H4, B7-H5, B7-H6, B7-H7, and ILDR2 and Their Receptors. Russ. J. Bioorgan. Chem. 2019;45:321–334. doi: 10.1134/S1068162019050091. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

