Circulating GLP-1 Levels as a Potential Indicator of Metabolic Syndrome Risk in Adult Women
- PMID: 33800785
- PMCID: PMC8001839
- DOI: 10.3390/nu13030865
Circulating GLP-1 Levels as a Potential Indicator of Metabolic Syndrome Risk in Adult Women
Abstract
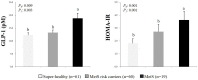
Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), an incretin hormone, plays an important role in regulating glucose homeostasis. In this study, the applicability of circulating GLP-1 levels as an early indicator of metabolic syndrome (MetS) risk was examined. Women without diagnosed diseases were grouped according to their number of MetS risk factors (MetS RFs) (no RFs as Super-healthy, n = 61; one or two RFs as MetS risk carriers, n = 60; 3 ≤ RFs as MetS, n = 19). The circulating GLP-1 levels and homeostasis model assessment insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) scores were significantly higher in the MetS group than in the other two groups. The GLP-1 levels correlated positively with adiposity, HOMA-IR, blood pressure, and high sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP), but not with fasting glucose and lipid profiles, whose significances were maintained after adjustments for age, smoking and drinking habits, menopausal status, and total calorie intake. The GLP-1 levels also increased proportionally with the number of MetS RFs. In the MetS group, the GLP-1 levels were much higher in individuals with obesity (body mass index ≥ 25 kg/m2). In conclusion, the circulating GLP-1 level may be applicable as a potential early indicator of MetS risk in women without diagnosed diseases. Further study with a large population is needed to confirm the conclusion.
Keywords: early indicator; glucagon-like peptide-1; metabolic syndrome; women.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures


References
-
- Alberti K.G.M.M., Eckel R.H., Grundy S.M., Zimmet P.Z., Cleeman J.I., Donato K.A., Fruchart J.C., James W.P.T., Loria C.M., Smith S.C., Jr. Harmonizing the metabolic syndrome: A joint interim statement of the International Diabetes Federation Task Force on Epi-demiology and Prevention; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; American Heart Association; World Heart Federation; International Atherosclerosis Society; and International Association for the Study of Obesity. Circulation. 2009;120:1640–1645. - PubMed
-
- Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey National Health Statistics: 2018 Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. [(accessed on 18 December 2020)]; Available online: https://knhanes.cdc.go.kr/knhanes/sub04/sub04_03.do.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

