Idiosyncratic Drug-Induced Liver Injury (DILI) and Herb-Induced Liver Injury (HILI): Diagnostic Algorithm Based on the Quantitative Roussel Uclaf Causality Assessment Method (RUCAM)
- PMID: 33800917
- PMCID: PMC7999240
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics11030458
Idiosyncratic Drug-Induced Liver Injury (DILI) and Herb-Induced Liver Injury (HILI): Diagnostic Algorithm Based on the Quantitative Roussel Uclaf Causality Assessment Method (RUCAM)
Abstract
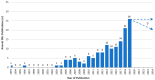
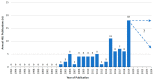
Causality assessment in liver injury induced by drugs and herbs remains a debated issue, requiring innovation and thorough understanding based on detailed information. Artificial intelligence (AI) principles recommend the use of algorithms for solving complex processes and are included in the diagnostic algorithm of Roussel Uclaf Causality Assessment Method (RUCAM) to help assess causality in suspected cases of idiosyncratic drug-induced liver injury (DILI) and herb-induced liver injury (HILI). From 1993 until the middle of 2020, a total of 95,865 DILI and HILI cases were assessed by RUCAM, outperforming by case numbers any other causality assessment method. The success of RUCAM can be traced back to its quantitative features with specific data elements that are individually scored leading to a final causality grading. RUCAM is objective, user friendly, transparent, and liver injury specific, with an updated version that should be used in future DILI and HILI cases. Support of RUCAM was also provided by scientists from China, not affiliated to any network, in the results of a scientometric evaluation of the global knowledge base of DILI. They highlighted the original RUCAM of 1993 and their authors as a publication quoted the greatest number of times and ranked first in the category of the top 10 references related to DILI. In conclusion, for stakeholders involved in DILI and HILI, RUCAM seems to be an effective diagnostic algorithm in line with AI principles.
Keywords: CAM; Roussel Uclaf Causality Assessment Method (RUCAM); artificial intelligence (AI); diagnostic algorithm; herb-induced liver injury (HILI); idiosyncratic drug-induced liver injury (DILI); quantitative RUCAM.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

