Associations between Circulating Markers of Cholesterol Homeostasis and Macrovascular Events among Patients Undergoing Hemodialysis
- PMID: 33801029
- PMCID: PMC8004048
- DOI: 10.3390/nu13031014
Associations between Circulating Markers of Cholesterol Homeostasis and Macrovascular Events among Patients Undergoing Hemodialysis
Abstract
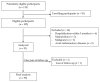
Current strategies targeting serum cholesterol bring limited benefits to mortality and macrovascular events prevention among hemodialysis patients. Direct measurements and analysis on circulating markers of cholesterol homeostasis could be promising solutions to this bottleneck. We prospectively enrolled 90 maintenance hemodialysis patients and 9 healthy controls in 2019 for 1 year. We measured circulating desmosterol and lathosterol as markers for cholesterol synthesis and campesterol and sitosterol for cholesterol absorption. At baseline, hemodialysis patients showed higher levels of campesterol (p = 0.023) compared to healthy controls. During follow-up, we identified 14 (15.4%) patients who experienced macrovascular events. Comparisons of cholesterol homeostasis markers between cohorts with and without macrovascular events showed no significant differences in markers of cholesterol synthesis or absorption. Using logistic regression analysis, the odds ratio was not statistically significant for the prediction of macrovascular events after full-adjusting for age, sex, diabetes, serum albumin, cholesterol, and triglyceride. We concluded that hemodialysis patients demonstrated higher level of cholesterols absorption, indicated by circulating campesterol compared to healthy subjects. Markers for cholesterol homeostasis were not significantly associated with macrovascular events during a 1-year follow-up. Our results shed light on the novel therapeutic target of modulating cholesterol absorption in HD patients.
Keywords: cholesterol homeostasis; hemodialysis; macrovascular events; mortality.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
-
- Hou F., Jiang J., Chen J., Yu X., Zhou Q., Chen P., Mei C., Xiong F., Shi W., Zhou W., et al. China collaborative study on dialysis: A multi-centers cohort study on cardiovascular diseases in patients on maintenance dialysis. BMC Nephrol. 2012;13:94. doi: 10.1186/1471-2369-13-94. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- United States Renal Data System . 2020 USRDS Annual Data Report: Epidemiology of Kidney Disease in the United States. National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases; Bethesda, MD, USA: 2020.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical