Can Hydrolysable Tannins in Diet of Entire Male Pigs Affect Carcass, Pork Quality Traits, Amino and Fatty Acid Profiles, and Boar Taint, Skatole and Androstenone Levels?
- PMID: 33801044
- PMCID: PMC8003867
- DOI: 10.3390/ani11030896
Can Hydrolysable Tannins in Diet of Entire Male Pigs Affect Carcass, Pork Quality Traits, Amino and Fatty Acid Profiles, and Boar Taint, Skatole and Androstenone Levels?
Abstract
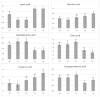
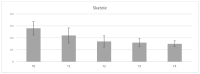
The slaughtering of entire males increases the probability of incidence of tainted pork due to the presence two main compounds-androstenone and skatole. If a surgical castration of young entire male pigs is stopped in the EU countries, fattening of boars is likely to become one of the most commonly used systems in pig farming. Since skatole production and accumulation in fat tissue can be controlled by dietary approaches, several studies have investigated various feed additives to reduce this compound of boar taint. Ones of the most promising is tannins. The aim of this study was to determine the effect of different dietary tannin level supplementation on carcass, pork quality, chemical, amino and fatty acid composition. as well as perception of boar taint and accumulation of skatole and androstenone in adipose tissue. Eighty entire males were randomly distributed to control (T0) and four experimental groups. Control pigs received standard feed mixture (16.8% CP, 13.9 MJ ME) without any tannin supplementation. Experimental pigs received the same diet with administration of 1% (T1), 2% (T2), 3% (T3) and 4% (T4)-sweet chestnut extract rich in hydrolysable tannins for 40 days (from average live weight of 80 kg until slaughter at average weight 122.28 kg ± 5.63 kg). Dietary tannins supplementation did not show any significant effect on chemical composition, cholesterol content, and amino acid composition of muscle as well as fatty acid composition and androstenone accumulation in adipose tissue. A slight or small effect was observed on carcass and meat quality, respectively. Pigs in groups T4 and/or T3-T4 had higher electrical conductivity in semimembranosus muscle and cooking loss value compared to T1, T2 or T0, T1, and T2 groups (p < 0.05). Tannins in the pig's diet greatly affected fatty acid profile in meat of entire males. The highest tannin levels (4%) increased concentrations of lauric, myristic, vaccenic, linoleic, total PUFA, and n-6 PUFA in muscle compared to the control. Similar results were found in group T3 except for vaccenic, linoleic, and total PUFA. On the contrary, concentrations of heptadecanoic and oleic acids in groups T3 and T4 were lower than those in T1 and T2 groups. Perception of boar taint using "hot iron" method (insertion a hot iron tip of soldering iron into adipose tissue) tended to decrease in T2 group compared with control. Skatole accumulation in fat tissue was reduced in groups T2-T4 at significance level (p = 0.052-0.055) compared to the control pigs. In summary, tannins supplementation had no effect on chemical and amino acid composition as well as fatty acid profile in adipose tissue, and only slight on carcass value. However, 4% concentration of tannins significantly increased content of some fatty acids compared to control group.
Keywords: boar taint; fatty acids; pig; skatole; tannin.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Dunshea F.R., Colantoni C., Howard K., McCauley I., Jackson P., Long K.A., Lopaticki S., Nugent E.A., Simons J.A., Walker J., et al. Vaccination of boars with a GnRH vaccine (Improvac) eliminates boar taint and increases growth performance. J. Anim. Sci. 2001;79:2524–2535. doi: 10.2527/2001.79102524x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Pauly C., Spring P., O’Doherty J.V., Ampuero Kragten S., Bee G. Growth performance, carcass characteristics and meat quality of group-penned surgically castrated, immunocastrated (Improvac®) and entire male pigs and individually penned entire male pigs. Animal. 2009;3:1057–1066. doi: 10.1017/S1751731109004418. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Daza A., Latorre M.A., Olivares A., López Bote C.J. The effects of male and female immunocastration on growth performances and carcass and meat quality of pigs intended for dry-cured ham production: A preliminary study. Livest. Sci. 2016;190:20–26. doi: 10.1016/j.livsci.2016.05.014. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

