Development of Injectable Polydactyly-Derived Chondrocyte Sheets
- PMID: 33801144
- PMCID: PMC8004148
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22063198
Development of Injectable Polydactyly-Derived Chondrocyte Sheets
Abstract
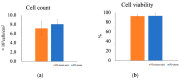
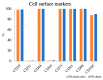
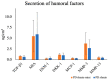
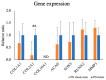
We are conducting a clinical study of the use of allogeneic polydactyly-derived chondrocyte sheets (PD sheets) for the repair of articular cartilage damage caused by osteoarthritis. However, the transplantation of PD sheets requires highly invasive surgery. To establish a less invasive treatment, we are currently developing injectable fragments of PD sheets (PD sheets-mini). Polydactyly-derived chondrocytes were seeded in RepCell™ or conventional temperature-responsive inserts and cultured. Cell counts and viability, histology, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qPCR), and flow cytometry were used to characterize PD sheets-mini and PD sheets collected from each culture. To examine the effects of injection on cell viability, PD sheets-mini were tested in four experimental conditions: non-injection control, 18 gauge (G) needle, 23G needle, and syringe only. PD sheets-mini produced similar amounts of humoral factors as PD sheets. No histological differences were observed between PD sheets and PD sheets-mini. Except for COL2A1, expression of cartilage-related genes did not differ between the two types of PD sheet. No significant differences were observed between injection conditions. PD sheets-mini have characteristics that resemble PD sheets. The cell viability of PD sheets-mini was not significantly affected by needle gauge size. Intra-articular injection may be a feasible, less invasive method to transplant PD sheets-mini.
Keywords: cartilage regeneration; cell sheet; minimally invasive treatment; osteoarthritis.
Conflict of interest statement
M.S. receives research funding from CellSeed Inc.
Figures



References
-
- Buckwalter J.A., Mankin H.J. Articular Cartilage: Tissue Design and Chondrocyte-Matrix Interactions. Instr. Course Lect. 1998;47:477–486. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) The World Health Report 2002–Reducing Risks, Promoting Healthy Life, Annex Table 3 Burden of disease in DALYs by Cause, Sex and Mortality Stratum in WHO Regions, Estimates for 2001, 196–197. [(accessed on 24 January 2021)];2002 Available online: https://www.who.int/whr/2002/en/
-
- Yoshimura N., Muraki S., Oka H., Mabuchi A., En-Yo Y., Yoshida M., Saika A., Yoshida H., Suzuki T., Yamamoto S., et al. Prevalence of Knee Osteoarthritis, Lumbar Spondylosis, and Osteoporosis in Japanese Men and Women: The Research on Osteoarthritis/Osteoporosis against Disability Study. J. Bone Min. Metab. 2009;27:620–628. doi: 10.1007/s00774-009-0080-8. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

