Identification of a Sesquiterpene Lactone from Arctium lappa Leaves with Antioxidant Activity in Primary Human Muscle Cells
- PMID: 33801315
- PMCID: PMC7958318
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26051328
Identification of a Sesquiterpene Lactone from Arctium lappa Leaves with Antioxidant Activity in Primary Human Muscle Cells
Abstract
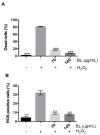
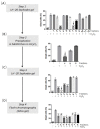
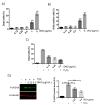
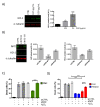
Many pathologies affecting muscles (muscular dystrophies, sarcopenia, cachexia, renal insufficiency, obesity, diabetes type 2, etc.) are now clearly linked to mechanisms involving oxidative stress. In this context, there is a growing interest in exploring plants to find new natural antioxidants to prevent the appearance and the development of these muscle disorders. In this study, we investigated the antioxidant properties of Arctium lappa leaves in a model of primary human muscle cells exposed to H2O2 oxidative stress. We identified using bioassay-guided purification, onopordopicrin, a sesquiterpene lactone as the main molecule responsible for the antioxidant activity of A. lappa leaf extract. According to our findings, onopordopicrin inhibited the H2O2-mediated loss of muscle cell viability, by limiting the production of free radicals and abolishing DNA cellular damages. Moreover, we showed that onopordopicrin promoted the expression of the nuclear factor-erythroid-2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) downstream target protein heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) in muscle cells. By using siRNA, we demonstrated that the inhibition of the expression of Nrf2 reduced the protective effect of onopordopicrin, indicating that the activation of the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway mediates the antioxidant effect of onopordopicrin in primary human muscle cells. Therefore, our results suggest that onopordopicrin may be a potential therapeutic molecule to fight against oxidative stress in pathological specific muscle disorders.
Keywords: Arctium lappa L.; antioxidant; burdock leaves; human myoblasts; onopordopicrin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Anti-ulcerogenic mechanisms of the sesquiterpene lactone onopordopicrin-enriched fraction from Arctium lappa L. (Asteraceae): role of somatostatin, gastrin, and endogenous sulfhydryls and nitric oxide.J Med Food. 2012 Apr;15(4):378-83. doi: 10.1089/jmf.2011.0025. Epub 2011 Dec 22. J Med Food. 2012. PMID: 22191571
-
Phytotoxic activity of crop residues from Burdock and an active substance.J Environ Sci Health B. 2019;54(11):877-882. doi: 10.1080/03601234.2019.1636600. Epub 2019 Jul 4. J Environ Sci Health B. 2019. PMID: 31271331
-
Hemistepsin A protects human keratinocytes against hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress through activation of the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2020 Sep 30;691:108512. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2020.108512. Epub 2020 Jul 24. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2020. PMID: 32712291
-
Phytochemicals and Biological Activities of Burdock (Arctium lappa L.) Extracts: A Review.Chem Biodivers. 2022 Nov;19(11):e202200615. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.202200615. Epub 2022 Nov 3. Chem Biodivers. 2022. PMID: 36198078 Review.
-
Arctium lappa (Burdock): Insights from ethnopharmacology potential, chemical constituents, clinical studies, pharmacological utility and nanomedicine.Biomed Pharmacother. 2023 Feb;158:114104. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.114104. Epub 2022 Dec 12. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023. PMID: 36516694 Review.
Cited by
-
The Effects of Antioxidants from Natural Products on Obesity, Dyslipidemia, Diabetes and Their Molecular Signaling Mechanism.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 12;23(4):2056. doi: 10.3390/ijms23042056. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35216172 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Network of Processes for Biorefining Burdock Seeds and Roots.Molecules. 2024 Feb 21;29(5):937. doi: 10.3390/molecules29050937. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38474449 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Sesquiterpene Lactone Xanthatin-13-(pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid) Isolated from Burdock Leaf Up-Regulates Cells' Oxidative Stress Defense Pathway.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Oct 14;10(10):1617. doi: 10.3390/antiox10101617. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34679753 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cacciapuoti F. Oxidative stress as “mother” of many human diseases at strong clinical impact. J. Cardiovasc. Med. Cardiol. 2016;3:001–006. doi: 10.17352/2455-2976.000020. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

