Cybervictimization and Adolescent Internet Addiction: A Moderated Mediation Model
- PMID: 33801345
- PMCID: PMC7967556
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph18052427
Cybervictimization and Adolescent Internet Addiction: A Moderated Mediation Model
Abstract
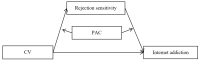
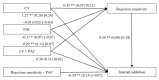
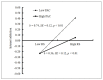
Previous research indicates that cybervictimization can lead to adolescent Internet addiction; however, there is a gap in the knowledge about the mediating and moderating variables facilitating this relationship. This study examines the role of rejection sensitivity as a mediator in this relationship and the role of parent-adolescent communication as a moderator for this mediation effect among Chinese adolescents. Participants were 1006 adolescents (M = 13.16 years, SD = 0.67), who completed the questionnaires anonymously. The questionnaires assessed the four variables of interest. Descriptive statistics and structural equation modeling were used for data analysis. The results show that the positive association between cybervictimization and adolescent Internet addiction is mediated by rejection sensitivity. Moreover, this indirect effect is stronger for adolescents with low parent-adolescent communication than for those with high parent-adolescent communication.
Keywords: adolescent; cybervictimization; internet addiction; parent–adolescent communication; rejection sensitivity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Parent-Adolescent Communication, School Engagement, and Internet Addiction among Chinese Adolescents: The Moderating Effect of Rejection Sensitivity.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Mar 29;18(7):3542. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18073542. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 33805480 Free PMC article.
-
Cybervictimization, Depression, and Adolescent Internet Addiction: The Moderating Effect of Prosocial Peer Affiliation.Front Psychol. 2020 Sep 29;11:572486. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2020.572486. eCollection 2020. Front Psychol. 2020. PMID: 33117238 Free PMC article.
-
Parent-adolescent relationship and adolescent internet addiction: A moderated mediation model.Addict Behav. 2018 Sep;84:171-177. doi: 10.1016/j.addbeh.2018.04.015. Epub 2018 Apr 24. Addict Behav. 2018. PMID: 29709874
-
The Association between Moral Intelligence and Communication Skills with Internet Addiction: The Mediating Role of Psychological Distress in Secondary School Students of Tabriz, Iran.J Caring Sci. 2024 Sep 29;14(1):42-51. doi: 10.34172/jcs.025.33745. eCollection 2025 Feb. J Caring Sci. 2024. PMID: 40391314 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The association between parent-child relationship and problematic internet use among English- and Chinese-language studies: A meta-analysis.Front Psychol. 2022 Aug 29;13:885819. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.885819. eCollection 2022. Front Psychol. 2022. PMID: 36110283 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The relationship between family functioning and social media addiction among university students: a moderated mediation model of depressive symptoms and peer support.BMC Psychol. 2024 Jun 10;12(1):341. doi: 10.1186/s40359-024-01818-2. BMC Psychol. 2024. PMID: 38858753 Free PMC article.
-
A Systematic Review of Parent-Child Communication Measures: Instruments and Their Psychometric Properties.Clin Child Fam Psychol Rev. 2023 Mar;26(1):121-142. doi: 10.1007/s10567-022-00414-3. Epub 2022 Sep 27. Clin Child Fam Psychol Rev. 2023. PMID: 36166179 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Relationship Between Cyberbullying and Technology Addiction in Adolescents.Public Health Nurs. 2025 Jan-Feb;42(1):33-43. doi: 10.1111/phn.13433. Epub 2024 Sep 30. Public Health Nurs. 2025. PMID: 39345215 Free PMC article.
-
Peer rejection and internet gaming disorder: the mediating role of relative deprivation and the moderating role of grit.Front Psychol. 2025 Jan 15;15:1415666. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1415666. eCollection 2024. Front Psychol. 2025. PMID: 39881688 Free PMC article.
-
Cognitive bias toward the Internet: The causes of adolescents' Internet addiction under parents' self-affirmation consciousness.Front Psychol. 2022 Aug 1;13:891473. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.891473. eCollection 2022. Front Psychol. 2022. PMID: 35978789 Free PMC article.
References
-
- China Internet Network Information Center “The 47th Statistical Report on Internet Development in China”. [(accessed on 3 February 2020)]; Available online: http://www.gov.cn/xinwen/2021-02/03/content_5584518.htm.
-
- Demir Y., Kutlu M. Relationships among Internet addiction, academic motivation, academic procrastination and school attachment in adolescents. Int. Online J. Educ. Sci. 2018;10:315–332. doi: 10.15345/iojes.2018.05.020. - DOI
-
- Kostak M.A., Dindar İ., Dinçkol R.Z. Loneliness, depression, social support levels, and other factors involving the Internet use of high school students in Turkey. Int. J. Ment. Health Addic. 2019;17:1521–1534. doi: 10.1007/s11469-018-9927-3. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

