SARS-CoV-2 Infection Is Asymptomatic in Nearly Half of Adults with Robust Anti-Spike Protein Receptor-Binding Domain Antibody Response
- PMID: 33801380
- PMCID: PMC7998869
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines9030207
SARS-CoV-2 Infection Is Asymptomatic in Nearly Half of Adults with Robust Anti-Spike Protein Receptor-Binding Domain Antibody Response
Abstract
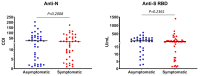
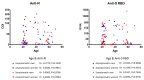
Between June and November 2020, we assessed plasma antibodies against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) nucleocapsid protein in 4996 participants (aged 18-82 years, 34.5% men) from the National and Kapodistrian University of Athens. The weighted overall prevalence was 1.6% and monthly prevalence correlated with viral RNA-confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infections in Greece, in the same period. Notably, 49% of seropositive cases reported no history of SARS-CoV-2 infection-related clinical symptoms and 33% were unsuspected of their previous infection. Additionally, levels of anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies against the spike-protein receptor-binding domain were similar between symptomatic and asymptomatic individuals, irrespective of age and gender. Using Food and Drug Administration Emergency Use Authorization-approved assays, these results support the need for such studies on pandemic evaluation and highlight the development of robust humoral immune responses even among asymptomatic individuals. The high percentage of unsuspected/asymptomatic active cases, which may contribute to community transmission for more days than that of cases who are aware and self-isolate, underscores the necessity of measures across the population for the efficient control of the pandemic.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2; antibodies; asymptomatic; seroepidemiology; unsuspected/asymptomatic.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests. Roche Diagnostics and NKUA-SARG had no role in the design, execution, interpretation, or writing of the study.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization . Weekly Epidemiological Update—15 December 2020. WHO; Geneva, Switzerland: 2020.
-
- Bi Q., Lessler J., Eckerle I., Lauer S.A., Kaiser L., Vuilleumier N., Cummings D.A.T., Flahault A., Petrovic D., Guessous I., et al. Household transmission of SARS-CoV-2: Insights from a population-based serological survey. MedRxiv Preprint. 2020 doi: 10.1101/2020.11.04.20225573. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Buitrago-Garcia D., Egli-Gany D., Counotte M.J., Hossmann S., Imeri H., Ipekci A.M., Salanti G., Low N. Occurrence and transmission potential of asymptomatic and presymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infections: A living systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS Med. 2020;17:e1003346. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1003346. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

