The Pluripotent Activities of Caffeic Acid Phenethyl Ester
- PMID: 33801469
- PMCID: PMC7958844
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26051335
The Pluripotent Activities of Caffeic Acid Phenethyl Ester
Abstract
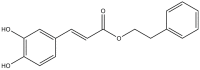
Caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE) is a strong antioxidant extracted from honey bee-hive propolis. The mentioned compound, a well-known NF-κB inhibitor, has been used in traditional medicine as a potent anti-inflammatory agent. CAPE has a broad spectrum of biological properties including anti-viral, anti-bacterial, anti-cancer, immunomodulatory, and wound-healing activities. This review characterizes published data about CAPE biological properties and potential therapeutic applications, that can be used in various diseases.
Keywords: NF-κB; antioxidant; caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE); inflammation; propolis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Wei X., Ma Z., Fontanilla C.V., Zhao L., Xu Z.C., Taggliabraci V., Johnstone B.H., Dodel R.C., Farlow M.R., Du Y. Caffeic acid phenethyl ester prevents cerebellar granule neurons (CGNs) against glutamate-induced neurotoxicity. Neuroscience. 2008;155:1098–1105. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.06.056. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ryoo S.W., Kim D.U., Won M., Chung K.S., Jang Y.J., Oh G.T., Park S.K., Maeng P.J., Yoo H.S., Hoe K.L. Native LDL induces inerleukin-8 expression via H2O2, p38 Kinase, and activator protein-1 in human aortic smooth muscle cells. Cardiovasc. Res. 2004;62:185–193. doi: 10.1016/j.cardiores.2004.01.002. - DOI - PubMed
-
- [(accessed on 20 December 2020)]; Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Caffeic_acid_phenethyl_ester#s....
-
- Tolba M.F., Azab S.S., Khalifa A.E., Abdel-Rahman S.Z., Abdel-Naim A.B. Caffeic acid phenethyl ester, a promising component of propolis with a plethora of biolobical activities: A review on its anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective, hepatoprotective, and cardioprotective effects. IUBMB Life. 2013;65:699–709. doi: 10.1002/iub.1189. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical