Arginine Decarboxylase Is Essential for Pneumococcal Stress Responses
- PMID: 33801541
- PMCID: PMC7998104
- DOI: 10.3390/pathogens10030286
Arginine Decarboxylase Is Essential for Pneumococcal Stress Responses
Abstract
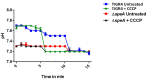
Polyamines such as putrescine, cadaverine, and spermidine are small cationic molecules that play significant roles in cellular processes, including bacterial stress responses and host-pathogen interactions. Streptococcus pneumoniae is an opportunistic human pathogen, which causes several diseases that account for significant morbidity and mortality worldwide. As it transits through different host niches, S. pneumoniae is exposed to and must adapt to different types of stress in the host microenvironment. We earlier reported that S. pneumoniae TIGR4, which harbors an isogenic deletion of an arginine decarboxylase (ΔspeA), an enzyme that catalyzes the synthesis of agmatine in the polyamine synthesis pathway, has a reduced capsule. Here, we report the impact of arginine decarboxylase deletion on pneumococcal stress responses. Our results show that ΔspeA is more susceptible to oxidative, nitrosative, and acid stress compared to the wild-type strain. Gene expression analysis by qRT-PCR indicates that thiol peroxidase, a scavenger of reactive oxygen species and aguA from the arginine deiminase system, could be important for peroxide stress responses in a polyamine-dependent manner. Our results also show that speA is essential for endogenous hydrogen peroxide and glutathione production in S. pneumoniae. Taken together, our findings demonstrate the critical role of arginine decarboxylase in pneumococcal stress responses that could impact adaptation and survival in the host.
Keywords: Streptococcus pneumoniae; acid stress; arginine decarboxylase; nitrosative stress; oxidative stress; polyamines.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
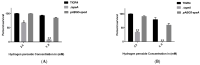



References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

