Evidence of Antimicrobial Resistance and Presence of Pathogenicity Genes in Yersinia enterocolitica Isolate from Wild Boars
- PMID: 33801613
- PMCID: PMC8065425
- DOI: 10.3390/pathogens10040398
Evidence of Antimicrobial Resistance and Presence of Pathogenicity Genes in Yersinia enterocolitica Isolate from Wild Boars
Abstract
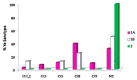
Yersinia enterocolitica (Ye) is a very important zoonosis andwild boars play a pivotal role in its transmission. In the last decade, the wild boar population has undergone a strong increase that haspushed them towards urbanized areas, facilitating the human-wildlife interface and the spread of infectious diseases from wildlife to domestic animals and humans. Therefore, it is important to know the serotype, antimicrobial resistance and presence of pathogenicity genes of Yersinia enterocolitica (Ye) isolated in species. From 2013 to 2018, we analyzed the liver of 4890 wild boars hunted in Liguria region; we isolated and serotyped 126 Ye positive samples. A decisive role in the pathogenicity is given by the presence of virulence genes; in Ye isolated we found ystB (~70%), ymoA (45.2%), ail (43.6%) and ystA (~20%). Moreover, we evaluated the susceptibility at various antimicrobic agents (Ampicillin, Chloramphenicol, Enrofloxacin, Gentamicin, Kanamycin, Trimethoprim-Sulfamethoxazole, Sulfisoxazole, Ceftiofur and Tetracycline). The antibiotic resistance was analyzed, and we found a time-dependent increase. It is important to shed light on the role of the wild boars as a reserve of potentially dangerous diseases for humans, and also on the antibiotic resistance that represents a public health problem.
Keywords: Yersinia enterocolitica; antibiotic-resistance; biotypes; pathogenicity; wild boar.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prevalence, bioserotyping and antibiotic resistance of pathogenic Yersinia enterocolitica detected in pigs at slaughter in Sardinia.Int J Food Microbiol. 2018 Oct 20;283:1-6. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2018.06.010. Epub 2018 Jun 13. Int J Food Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29929063
-
Virulence-associated gene pattern of porcine and human Yersinia enterocolitica biotype 4 isolates.Int J Food Microbiol. 2015 Apr 2;198:70-4. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2014.12.029. Epub 2014 Dec 30. Int J Food Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25617775
-
Prevalence, Virulence and Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Salmonella spp., Yersinia enterocolitica and Listeria monocytogenes in European Wild Boar (Sus scrofa) Hunted in Tuscany (Central Italy).Pathogens. 2021 Jan 20;10(2):93. doi: 10.3390/pathogens10020093. Pathogens. 2021. PMID: 33498307 Free PMC article.
-
The prevalence, characterisation, and antimicrobial resistance of Yersinia enterocolitica in pigs from Central Italy.Vet Ital. 2018 Jun 30;54(2):115-123. doi: 10.12834/VetIt.1126.6109.2. Vet Ital. 2018. PMID: 30019328
-
Yersinia pseudotuberculosis Prevalence and Diversity in Wild Boars in Northeast Germany.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2018 Aug 31;84(18):e00675-18. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00675-18. Print 2018 Sep 15. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29980552 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Characterisation of Yersinia Enterocolitica Strains Isolated from Wildlife in the Northwestern Italian Alps.J Vet Res. 2022 Apr 22;66(2):141-149. doi: 10.2478/jvetres-2022-0021. eCollection 2022 Jun. J Vet Res. 2022. PMID: 35892105 Free PMC article.
-
Hunted Wild Boars in Sardinia: Prevalence, Antimicrobial Resistance and Genomic Analysis of Salmonella and Yersinia enterocolitica.Foods. 2023 Dec 23;13(1):65. doi: 10.3390/foods13010065. Foods. 2023. PMID: 38201093 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the Correlation between the mRNA Expression Levels of ystA and ymoA Genes in Y. enterocolitica Strains with Different Enterotoxic Properties.Pathogens. 2021 Sep 3;10(9):1136. doi: 10.3390/pathogens10091136. Pathogens. 2021. PMID: 34578168 Free PMC article.
-
Higher Resistance of Yersinia enterocolitica in Comparison to Yersinia pseudotuberculosis to Antibiotics and Cinnamon, Oregano and Thyme Essential Oils.Pathogens. 2022 Dec 1;11(12):1456. doi: 10.3390/pathogens11121456. Pathogens. 2022. PMID: 36558790 Free PMC article.
-
Detection and Characterization of Zoonotic Pathogens in Game Meat Hunted in Northwestern Italy.Animals (Basel). 2024 Feb 7;14(4):562. doi: 10.3390/ani14040562. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38396530 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wauters G., Vandecasteele C., Strijckmans K., Hoste J. Determination of cadmium, thallium and lead in environmental samples by proton activation analysis. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 1987;112:23–31. doi: 10.1007/BF02037273. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

