Chemical Diversity and Biological Activity of Secondary Metabolites Isolated from Indonesian Marine Invertebrates
- PMID: 33801617
- PMCID: PMC8037762
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26071898
Chemical Diversity and Biological Activity of Secondary Metabolites Isolated from Indonesian Marine Invertebrates
Abstract
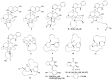
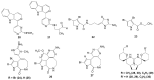
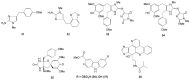
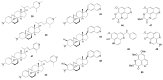
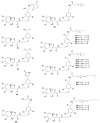
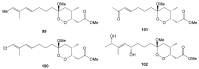
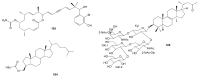
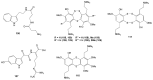
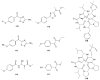
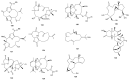
Marine invertebrates have been reported to be an excellent resource of many novel bioactive compounds. Studies reported that Indonesia has remarkable yet underexplored marine natural products, with a high chemical diversity and a broad spectrum of biological activities. This review discusses recent updates on the exploration of marine natural products from Indonesian marine invertebrates (i.e., sponges, tunicates, and soft corals) throughout 2007-2020. This paper summarizes the structural diversity and biological function of the bioactive compounds isolated from Indonesian marine invertebrates as antimicrobial, antifungal, anticancer, and antiviral, while also presenting the opportunity for further investigation of novel compounds derived from Indonesian marine invertebrates.
Keywords: Indonesia; biodiversity; biological activity; marine invertebrates; marine natural product; soft corals; sponges; tunicates.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there is no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Jha R., Zi-rong X. Biomedical Compounds from Marine Organisms. Mar. Drugs. 2004;2:123–146. doi: 10.3390/md203123. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

