Potential Role of Nanoparticles in Treating the Accumulation of Amyloid-Beta Peptide in Alzheimer's Patients
- PMID: 33801619
- PMCID: PMC8036916
- DOI: 10.3390/polym13071051
Potential Role of Nanoparticles in Treating the Accumulation of Amyloid-Beta Peptide in Alzheimer's Patients
Abstract
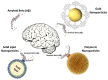
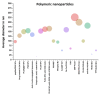
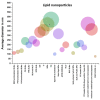
The disorder of Alzheimer's is marked by progressive pathophysiological neurodegeneration. The amino acid peptides in the amyloid plaques found in the brains of people with Alzheimer's disease (AD) are known as amyloid-beta (Aβ). Current treatments are not curative, and the effects associated with AD are reduced. Improving treatment results involved the targeting of drugs at optimum therapeutic concentration. Nanotechnology is seen as an unconventional, modern technology that plays a key role in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease. Using nanoparticles, molecular detection, effective drug targeting, and their combination offer high sensitivity. The aim of this review is to shed light on the function and successful role of nanoparticles to resolve Aβ aggregation and thus to help cure Alzheimer's disease. The analysis divides these nanoparticles into three categories: polymer, lipid, and gold nanoparticles. A thorough comparison was then made between the nanoparticles, which are used according to their role, properties, and size in the procedure. The nanoparticles can prevent the accumulation of Aβ during the efficient delivery of the drug to the cells to treat Alzheimer's disease. Furthermore, this comparison demonstrated the ability of these nanoparticles to deal efficiently with Alzheimer's disease. The role of these nanoparticles varied from delivering the drug to brain cells to dealing with the disease-causing peptide.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s; amyloid beta-peptide; drug delivery; lipids; nanodrugs; nanoparticles.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Application of optogenetic Amyloid-β distinguishes between metabolic and physical damages in neurodegeneration.Elife. 2020 Mar 31;9:e52589. doi: 10.7554/eLife.52589. Elife. 2020. PMID: 32228858 Free PMC article.
-
Fibrillar Aβ triggers microglial proteome alterations and dysfunction in Alzheimer mouse models.Elife. 2020 Jun 8;9:e54083. doi: 10.7554/eLife.54083. Elife. 2020. PMID: 32510331 Free PMC article.
-
Alzheimer's disease.Subcell Biochem. 2012;65:329-52. doi: 10.1007/978-94-007-5416-4_14. Subcell Biochem. 2012. PMID: 23225010 Review.
-
A novel synthesis of selenium nanoparticles encapsulated PLGA nanospheres with curcumin molecules for the inhibition of amyloid β aggregation in Alzheimer's disease.J Photochem Photobiol B. 2019 Jan;190:98-102. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2018.11.008. Epub 2018 Nov 15. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2019. PMID: 30504054
-
Comparison of Tau and Amyloid-β Targeted Immunotherapy Nanoparticles for Alzheimer's Disease.Biomolecules. 2022 Jul 18;12(7):1001. doi: 10.3390/biom12071001. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 35883556 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Nanoenzyme Constructed from Manganese and Strandberg-Type Phosphomolybdate with Versatility in Antioxidant and Modulating Conformation of Aβ Protein Misfolding Aggregates In Vitro.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 21;24(5):4317. doi: 10.3390/ijms24054317. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36901748 Free PMC article.
-
Tanshinone-IIA mediated neuroprotection by modulating neuronal pathways.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2023 Aug;396(8):1647-1667. doi: 10.1007/s00210-023-02476-8. Epub 2023 Apr 3. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37010572 Review.
-
Nanoparticles loaded with natural medicines for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease.Front Neurosci. 2023 Oct 9;17:1112435. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1112435. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37877008 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In Vitro Regulation of Amyloid production in Alzheimer's Disease via Curcumin-Loaded Silver Nanoparticles with Antioxidant and Acetylcholinesterase-Inhibiting Properties.Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Jun 3. doi: 10.1007/s12035-025-05125-8. Online ahead of print. Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 40459716
-
Ion-activated In Situ Gel of Gellan Gum Containing Chrysin for Nasal Administration in Parkinson's Disease.Recent Adv Drug Deliv Formul. 2024;18(1):35-49. doi: 10.2174/0126673878279656231204103855. Recent Adv Drug Deliv Formul. 2024. PMID: 38058093
References
-
- Cai J., Dao P., Chen H., Yan L., Li Y., Zhang W., Li L., Du Z., Dong C., Meunier B. Ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles bound NIR dyes: Novel theranostic agents for Alzheimer’s disease. Dye. Pigment. 2020;173:107968. doi: 10.1016/j.dyepig.2019.107968. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

