Exercise-A Panacea of Metabolic Dysregulation in Cancer: Physiological and Molecular Insights
- PMID: 33801684
- PMCID: PMC8037630
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22073469
Exercise-A Panacea of Metabolic Dysregulation in Cancer: Physiological and Molecular Insights
Abstract
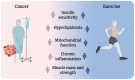
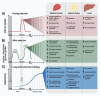
Metabolic dysfunction is a comorbidity of many types of cancers. Disruption of glucose metabolism is of concern, as it is associated with higher cancer recurrence rates and reduced survival. Current evidence suggests many health benefits from exercise during and after cancer treatment, yet only a limited number of studies have addressed the effect of exercise on cancer-associated disruption of metabolism. In this review, we draw on studies in cells, rodents, and humans to describe the metabolic dysfunctions observed in cancer and the tissues involved. We discuss how the known effects of acute exercise and exercise training observed in healthy subjects could have a positive outcome on mechanisms in people with cancer, namely: insulin resistance, hyperlipidemia, mitochondrial dysfunction, inflammation, and cachexia. Finally, we compile the current limited knowledge of how exercise corrects metabolic control in cancer and identify unanswered questions for future research.
Keywords: adipose tissue; cancer; cancer cachexia; exercise; insulin resistance; metabolism; skeletal muscle.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Rohdenburg G.L., Bernhard A., Krehbiel O. Sugar tolerance in cancer. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 1919;72:1528. doi: 10.1001/jama.1919.02610210024007. - DOI
-
- Luque R.M., López-Sánchez L.M., Villa-Osaba A., Luque I.M., Santos-Romero A.L., Yubero-Serrano E.M., Cara-García M., Álvarez-Benito M., López-Miranda J., Gahete M.D., et al. Breast cancer is associated to impaired glucose/insulin homeostasis in premenopausal obese/overweight patients. Oncotarget. 2017;8:81462–81474. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.20399. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

