Correlates of Vaccine-Induced Protection against SARS-CoV-2
- PMID: 33801831
- PMCID: PMC8035658
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines9030238
Correlates of Vaccine-Induced Protection against SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
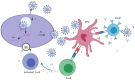
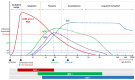
We are in the midst of a pandemic caused by the novel severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), which causes the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). SARS-CoV-2 has caused more than two million deaths after one year of the pandemic. The world is experiencing a deep economic recession. Safe and effective vaccines are needed to prevent further morbidity and mortality. Vaccine candidates against COVID-19 have been developed at an unprecedented speed, with more than 200 vaccine candidates currently under investigation. Among those, 20 candidates have entered the clinical Phase 3 to evaluate efficacy, and three have been approved by the European Medicines Agency. The aim of immunization is to act against infection, disease and/or transmission. However, the measurement of vaccine efficacy is challenging, as efficacy trials need to include large cohorts with verum and placebo cohorts. In the future, this will be even more challenging as further vaccine candidates will receive approval, an increasing number of humans will receive vaccinations and incidence might decrease. To evaluate novel and second-generation vaccine candidates, randomized placebo-controlled trials might not be appropriate anymore. Correlates of protection (CoP) could be an important tool to evaluate novel vaccine candidates, but vaccine-induced CoP have not been clearly defined for SARS-CoV-2 vaccines. In this review, we report on immunogenicity against natural SARS-CoV-2 infection, vaccine-induced immune responses and discuss immunological markers that can be linked to protection. By discussing the immunogenicity and efficacy of forerunner vaccines, we aim to give a comprehensive overview of possible efficacy measures and CoP.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; correlates of protection; immunogenicity; pandemic; vaccine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- WHO WHO Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Dashboard. [(accessed on 2 January 2021)];2021 Available online: https://covid19.who.int/
-
- WHO DRAFT Landscape of COVID-19 Candidate Vaccines. World Health Organization. [(accessed on 2 January 2021)];2020 Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/draft-landscape-of-covid-19-cand....
-
- LSHTM London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine—COVID-19 Vaccine Tracker 2020. [(accessed on 2 January 2021)]; Available online: https://vac-lshtm.shinyapps.io/ncov_vaccine_landscape/
-
- NYT Coronavirus Vaccine Tracker. The New York Times. Mar 2, 2021. [(accessed on 2 January 2021)]. Available online: https://www.nytimes.com/interactive/2020/science/coronavirus-vaccine-tra....
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

