Baicalin Represses Type Three Secretion System of Pseudomonas aeruginosa through PQS System
- PMID: 33801847
- PMCID: PMC8001617
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26061497
Baicalin Represses Type Three Secretion System of Pseudomonas aeruginosa through PQS System
Abstract
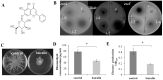
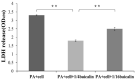
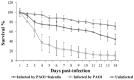
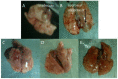
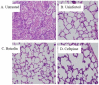
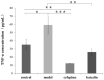
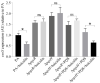
Therapeutics that target the virulence of pathogens rather than their viability offer a promising alternative for treating infectious diseases and circumventing antibiotic resistance. In this study, we searched for anti-virulence compounds against Pseudomonas aeruginosa from Chinese herbs and investigated baicalin from Scutellariae radix as such an active anti-virulence compound. The effect of baicalin on a range of important virulence factors in P. aeruginosa was assessed using luxCDABE-based reporters and by phenotypical assays. The molecular mechanism of the virulence inhibition by baicalin was investigated using genetic approaches. The impact of baicalin on P. aeruginosa pathogenicity was evaluated by both in vitro assays and in vivo animal models. The results show that baicalin diminished a plenty of important virulence factors in P. aeruginosa, including the Type III secretion system (T3SS). Baicalin treatment reduced the cellular toxicity of P. aeruginosa on the mammalian cells and attenuated in vivo pathogenicity in a Drosophila melanogaster infection model. In a rat pulmonary infection model, baicalin significantly reduced the severity of lung pathology and accelerated lung bacterial clearance. The PqsR of the Pseudomonas quinolone signal (PQS) system was found to be required for baicalin's impact on T3SS. These findings indicate that baicalin is a promising therapeutic candidate for treating P. aeruginosa infections.
Keywords: PQS inhibition; Pseudomonas aeruginosa; Type III secretion system; baicalin; mouse lung infection model; virulence factors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Baicalin inhibits biofilm formation, attenuates the quorum sensing-controlled virulence and enhances Pseudomonas aeruginosa clearance in a mouse peritoneal implant infection model.PLoS One. 2017 Apr 28;12(4):e0176883. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0176883. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28453568 Free PMC article.
-
Application of Dual Inhibition Concept within Looped Autoregulatory Systems toward Antivirulence Agents against Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infections.ACS Chem Biol. 2016 May 20;11(5):1279-86. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.6b00117. Epub 2016 Mar 1. ACS Chem Biol. 2016. PMID: 26882081
-
Traditional Chinese Medicine Monomer Bakuchiol Attenuates the Pathogenicity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa via Targeting PqsR.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 30;26(1):243. doi: 10.3390/ijms26010243. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39796099 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-PqsR compounds as next-generation antibacterial agents against Pseudomonas aeruginosa: A review.Eur J Med Chem. 2019 Jun 15;172:26-35. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.03.049. Epub 2019 Mar 25. Eur J Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 30939351 Review.
-
The third quorum-sensing system of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Pseudomonas quinolone signal and the enigmatic PqsE protein.J Med Microbiol. 2020 Jan;69(1):25-34. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.001116. J Med Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 31794380 Review.
Cited by
-
Natural products from traditional medicine as promising agents targeting at different stages of oral biofilm development.Front Microbiol. 2022 Aug 12;13:955459. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.955459. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36033896 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of baicalin on eradicating biofilms of bovine milk derived Acinetobacter lwoffii.BMC Vet Res. 2024 May 20;20(1):212. doi: 10.1186/s12917-024-04015-w. BMC Vet Res. 2024. PMID: 38764041 Free PMC article.
-
Drosophila melanogaster as an organism model for studying cystic fibrosis and its major associated microbial infections.Infect Immun. 2023 Nov 16;91(11):e0024023. doi: 10.1128/iai.00240-23. Epub 2023 Oct 17. Infect Immun. 2023. PMID: 37847031 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Baicalin-aluminum alleviates necrotic enteritis in broiler chickens by inhibiting virulence factors expression of Clostridium perfringens.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023 Sep 25;13:1243819. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1243819. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37818042 Free PMC article.
-
Peptidomimetics as Potential Anti-Virulence Drugs Against Resistant Bacterial Pathogens.Front Microbiol. 2022 Apr 18;13:831037. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.831037. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35516442 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Schulert G.S., Feltman H., Rabin S.D.P., Martin C.G., Battle S.E., Rello J., Hauser A.R. Secretion of the Toxin ExoU Is a Marker for Highly Virulent Pseudomonas aeruginosa Isolates Obtained from Patients with Hospital-Acquired Pneumonia. J. Infect. Dis. 2003;188:1695–1706. doi: 10.1086/379372. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

