Kidney-Targeted Epoxyeicosatrienoic Acid Analog, EET-F01, Reduces Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, and Cisplatin-Induced Nephrotoxicity
- PMID: 33801911
- PMCID: PMC7998941
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22062793
Kidney-Targeted Epoxyeicosatrienoic Acid Analog, EET-F01, Reduces Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, and Cisplatin-Induced Nephrotoxicity
Abstract
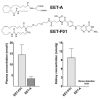
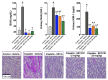
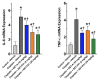
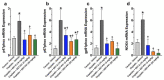
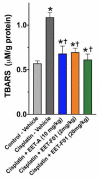
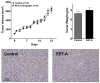
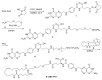
Although epoxyeicosatrienoic acid (EET) analogs have performed well in several acute and chronic kidney disease models, targeted delivery of EET analogs to the kidney can be reasonably expected to reduce the level of drug needed to achieve a therapeutic effect and obviate possible side effects. For EET analog kidney-targeted delivery, we conjugated a stable EET analog to folic acid via a PEG-diamine linker. Next, we compared the kidney targeted EET analog, EET-F01, to a well-studied EET analog, EET-A. EET-A or EET-F01 was infused i.v. and plasma and kidney tissue collected. EET-A was detected in the plasma but was undetectable in the kidney. On the other hand, EET-F01 was detected in the plasma and kidney. Experiments were conducted to compare the efficacy of EET-F01 and EET-A for decreasing cisplatin nephrotoxicity. Cisplatin was administered to WKY rats treated with vehicle, EET-A (10 mg/kg i.p.) or EET-F01 (20 mg/kg or 2 mg/kg i.p.). Cisplatin increased kidney injury markers, viz., blood urea nitrogen (BUN), N-acetyl-β-(D)-glucosaminidase (NAG), kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1), and thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS). EET-F01 was as effective as EET-A in decreasing BUN, NAG, KIM-1, TBARS, and renal histological injury caused by cisplatin. Despite its almost 2×-greater molecular weight compared with EET-A, EET-F01 was comparably effective in decreasing renal injury at a 10-fold w/w lower dose. EET-F01 decreased cisplatin nephrotoxicity by reducing oxidative stress and inflammation. These data demonstrate that EET-F01 targets the kidney, allows for a lower effective dose, and combats cisplatin nephrotoxicity. In conclusion, we have developed a kidney targeted EET analog, EET-F01, that demonstrates excellent potential as a therapeutic for kidney diseases.
Keywords: chemotherapy; epoxyeicosatrienoic acid; kidney-targeted; nephrotoxicity; novel therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
John D. Imig, Md. Abdul Hye Khan, Adeniyi Adebesin, and John R. Falck have patents that cover the composition of matter for EET-A and EET-F01. The authors declare no other conflict of interest, financial or otherwise.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

