Dual Inhibition of AKT and MEK Pathways Potentiates the Anti-Cancer Effect of Gefitinib in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells
- PMID: 33801977
- PMCID: PMC8000364
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers13061205
Dual Inhibition of AKT and MEK Pathways Potentiates the Anti-Cancer Effect of Gefitinib in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells
Abstract
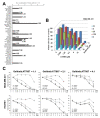
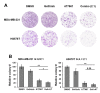
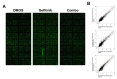
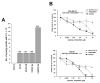
There is an unmet medical need for the development of new targeted therapeutic strategies for triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC). With drug combination screenings, we found that the triple combination of the protein kinase inhibitors (PKIs) of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), v-akt murine thymoma viral oncogene homolog (AKT), and MAPK/ERK kinase (MEK) is effective in inducing apoptosis in TNBC cells. A set of PKIs were first screened in combination with gefitinib in the TNBC cell line, MDA-MB-231. The AKT inhibitor, AT7867, was identified and further analyzed in two mesenchymal stem-like (MSL) subtype TNBC cells, MDA-MB-231 and HS578T. A combination of gefitinib and AT7867 reduced the proliferation and long-term survival of MSL TNBC cells. However, gefitinib and AT7867 induced the activation of the rat sarcoma (RAS)/ v-raf-1 murine leukemia viral oncogene homolog (RAF)/MEK/ extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) pathway. To inhibit this pathway, MEK/ERK inhibitors were further screened in MDA-MB-231 cells in the presence of gefitinib and AT7867. As a result, we identified that the MEK inhibitor, PD-0325901, further enhanced the anti-proliferative and anti-clonogenic effects of gefitinib and AT7867 by inducing apoptosis. Our results suggest that the dual inhibition of the AKT and MEK pathways is a novel potential therapeutic strategy for targeting EGFR in TNBC cells.
Keywords: AKT; EGFR resistance; MEK; anti-cancer; combination; protein kinase inhibitor (PKI); synergism; triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
EGFR and MEK Blockade in Triple Negative Breast Cancer Cells.J Cell Biochem. 2015 Dec;116(12):2778-85. doi: 10.1002/jcb.25220. J Cell Biochem. 2015. PMID: 25959272
-
Inhibition of the PI3K/AKT pathway potentiates cytotoxicity of EGFR kinase inhibitors in triple-negative breast cancer cells.J Cell Mol Med. 2013 May;17(5):648-56. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.12046. Epub 2013 Apr 20. J Cell Mol Med. 2013. PMID: 23601074 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of RPTOR overcomes resistance to EGFR inhibition in triple-negative breast cancer cells.Int J Oncol. 2018 Mar;52(3):828-840. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2018.4244. Epub 2018 Jan 15. Int J Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29344641
-
Immunomodulatory Properties of PI3K/AKT/mTOR and MAPK/MEK/ERK Inhibition Augment Response to Immune Checkpoint Blockade in Melanoma and Triple-Negative Breast Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 1;23(13):7353. doi: 10.3390/ijms23137353. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35806358 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of resistance to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2015 Sep;5(5):390-401. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2015.07.001. Epub 2015 Jul 26. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2015. PMID: 26579470 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Upregulation of the ferroptosis-related STEAP3 gene is a specific predictor of poor triple-negative breast cancer patient outcomes.Front Oncol. 2023 Mar 31;13:1032364. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1032364. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37064114 Free PMC article.
-
Endogenous pAKT activity is associated with response to AKT inhibition alone and in combination with immune checkpoint inhibition in murine models of TNBC.Cancer Lett. 2024 Apr 1;586:216681. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2024.216681. Epub 2024 Feb 3. Cancer Lett. 2024. PMID: 38311054 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Classification, Treatment, and Genetic Biomarkers in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: A Review.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2023 Jan-Dec;22:15330338221145246. doi: 10.1177/15330338221145246. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2023. PMID: 36601658 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Drug-Induced Resistance and Phenotypic Switch in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Can Be Controlled via Resolution and Targeting of Individualized Signaling Signatures.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Oct 6;13(19):5009. doi: 10.3390/cancers13195009. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34638492 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of IκB Kinase Is a Potential Therapeutic Strategy to Circumvent Resistance to Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Inhibition in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Oct 24;14(21):5215. doi: 10.3390/cancers14215215. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36358633 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

