Obtusifolin, an Anthraquinone Extracted from Senna obtusifolia (L.) H.S.Irwin & Barneby, Reduces Inflammation in a Mouse Osteoarthritis Model
- PMID: 33802005
- PMCID: PMC7999271
- DOI: 10.3390/ph14030249
Obtusifolin, an Anthraquinone Extracted from Senna obtusifolia (L.) H.S.Irwin & Barneby, Reduces Inflammation in a Mouse Osteoarthritis Model
Abstract
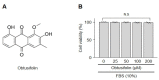
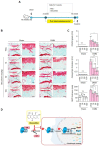
Osteoarthritis (OA) is an age-related degenerative disease that causes cartilage dysfunction and inflammation. Obtusifolin, an anthraquinone extracted from Senna obtusifolia (L.) H.S.Irwin & Barneby seeds, has anti-inflammatory functions; it could be used as a drug component to relieve OA symptoms. In this study, we investigated the effects of obtusifolin on OA inflammation. In vitro, interleukin (IL)-1β (1 ng/mL)-treated mouse chondrocytes were co-treated with obtusifolin at different concentrations. The expression of matrix metalloproteinase (Mmp) 3, Mmp13, cyclooxygenase 2 (Cox2), and signaling proteins was measured by polymerase chain reaction and Western blotting; collagenase activity and the PGE2 level were also determined. In vivo, OA-induced C57BL/6 mice were administered obtusifolin, and their cartilage was stained with Safranin O to observe damage. Obtusifolin inhibited Mmp3, Mmp13, and Cox2 expression to levels similar to or more than those after treatment with celecoxib. Additionally, obtusifolin decreased collagenase activity and the PGE2 level. Furthermore, obtusifolin regulated OA via the NF-κB signaling pathway. In surgically induced OA mouse models, the cartilage destruction decreased when obtusifolin was administered orally. Taken together, our results show that obtusifolin effectively reduces cartilage damage via the regulation of MMPs and Cox2 expression. Hence, we suggest that obtusifolin could be a component of another OA symptom reliever.
Keywords: NF-κB; inflammation; obtusifolin; osteoarthritis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Schisandrin A Inhibits the IL-1β-Induced Inflammation and Cartilage Degradation via Suppression of MAPK and NF-κB Signal Pathways in Rat Chondrocytes.Front Pharmacol. 2019 Jan 29;10:41. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00041. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30761007 Free PMC article.
-
Alpha-Mangostin protects rat articular chondrocytes against IL-1β-induced inflammation and slows the progression of osteoarthritis in a rat model.Int Immunopharmacol. 2017 Nov;52:34-43. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2017.08.010. Epub 2017 Aug 31. Int Immunopharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28858724
-
Salvianolic acid B inhibits IL-1β-induced inflammatory cytokine production in human osteoarthritis chondrocytes and has a protective effect in a mouse osteoarthritis model.Int Immunopharmacol. 2017 May;46:31-37. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2017.02.021. Epub 2017 Feb 27. Int Immunopharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28254683
-
Paeonol Inhibits IL-1β-Induced Inflammation via PI3K/Akt/NF-κB Pathways: In Vivo and Vitro Studies.Inflammation. 2017 Oct;40(5):1698-1706. doi: 10.1007/s10753-017-0611-8. Inflammation. 2017. PMID: 28695367
-
Cryptotanshinone protects against IL-1β-induced inflammation in human osteoarthritis chondrocytes and ameliorates the progression of osteoarthritis in mice.Int Immunopharmacol. 2017 Sep;50:161-167. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2017.06.017. Epub 2017 Jun 27. Int Immunopharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28666239
Cited by
-
Obtusifolin improves cisplatin-induced hepatonephrotoxicity via the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Aug;398(8):10337-10352. doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-03900-x. Epub 2025 Feb 20. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39976722 Free PMC article.
-
Obtusifolin inhibits podocyte apoptosis by inactivating NF-κB signaling in acute kidney injury.Cytotechnology. 2024 Oct;76(5):559-569. doi: 10.1007/s10616-024-00638-x. Epub 2024 Jun 21. Cytotechnology. 2024. PMID: 39188647
-
Blockade of ZMIZ1-GATA4 Axis Regulation Restores Youthfulness to Aged Cartilage.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025 Apr;12(16):e2404311. doi: 10.1002/advs.202404311. Epub 2025 Mar 5. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025. PMID: 40040621 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome and HPLC Analysis Reveal the Regulatory Mechanisms of Aurantio-Obtusin in Space Environment-Induced Senna obtusifolia Lines.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Jan 14;19(2):898. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19020898. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35055719 Free PMC article.
-
Potent and Selective Inhibition of CYP1A2 Enzyme by Obtusifolin and Its Chemopreventive Effects.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Dec 1;14(12):2683. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14122683. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 36559174 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

